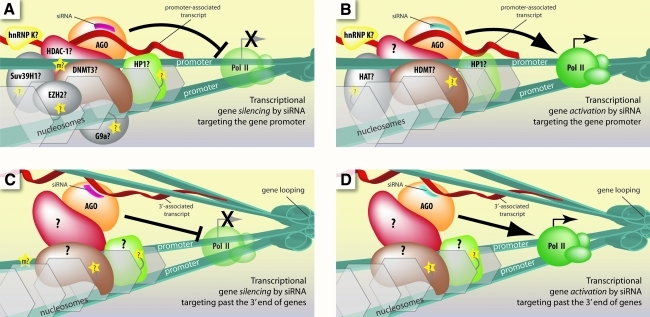
FIG. 5.
Current models for the molecular mechanism of transcriptional control by small RNAs that target gene promoters and regions past the 3′ end of genes in mammalian cells. (A, B) Promoter-targeted siRNAs guide AGO protein to promoter-associated transcripts. A number of chromatin modification and remodeling enzymes have been implicated in this process and are recruited to either silence or activate gene expression. (C, D) siRNAs targeted to regions past the 3′-ends of genes can guide AGO to noncoding transcripts overlapping those regions. Gene looping, which brings the 3′-end into close proximity to the promoter, enables recruitment of factors that can remodel or modify the promoter chromatin to modulate RNA polymerase II activity, either repressing or activating transcription.