Abstract
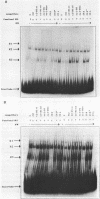
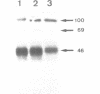
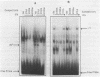
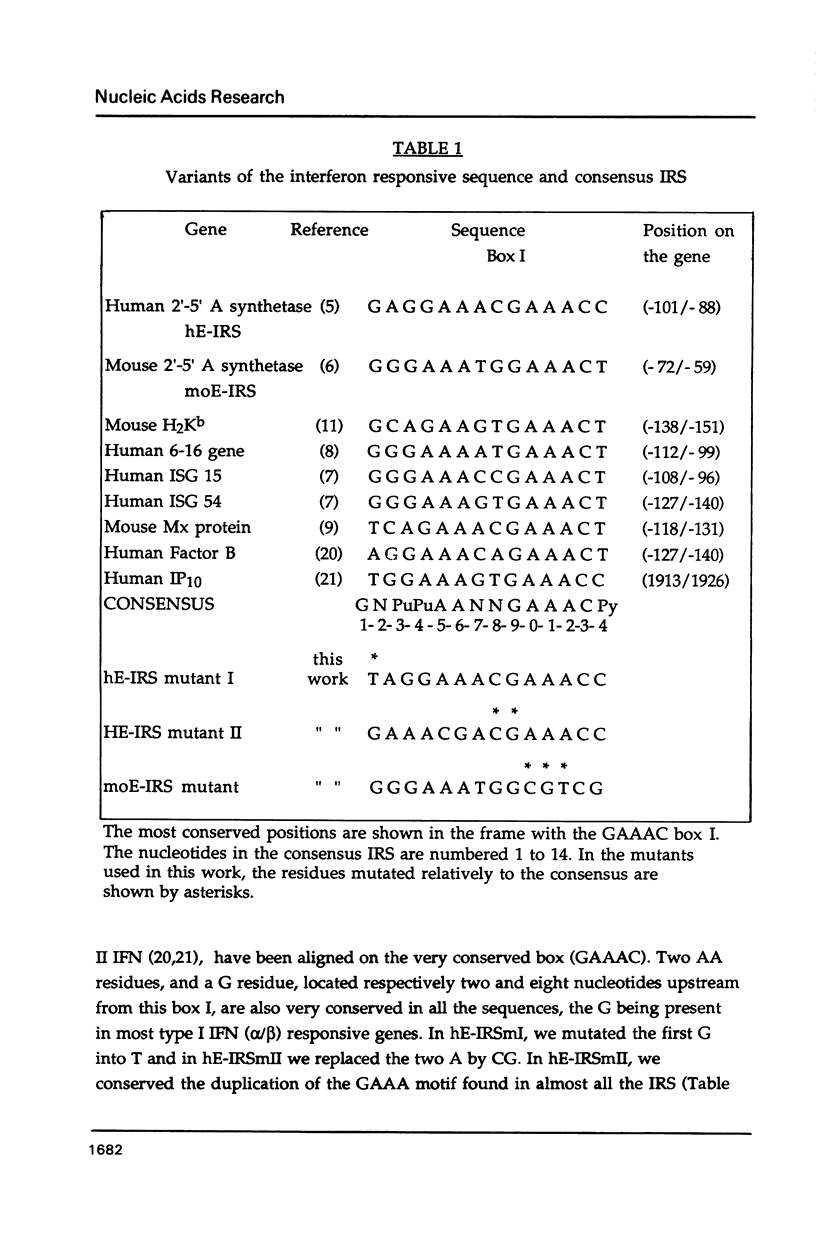
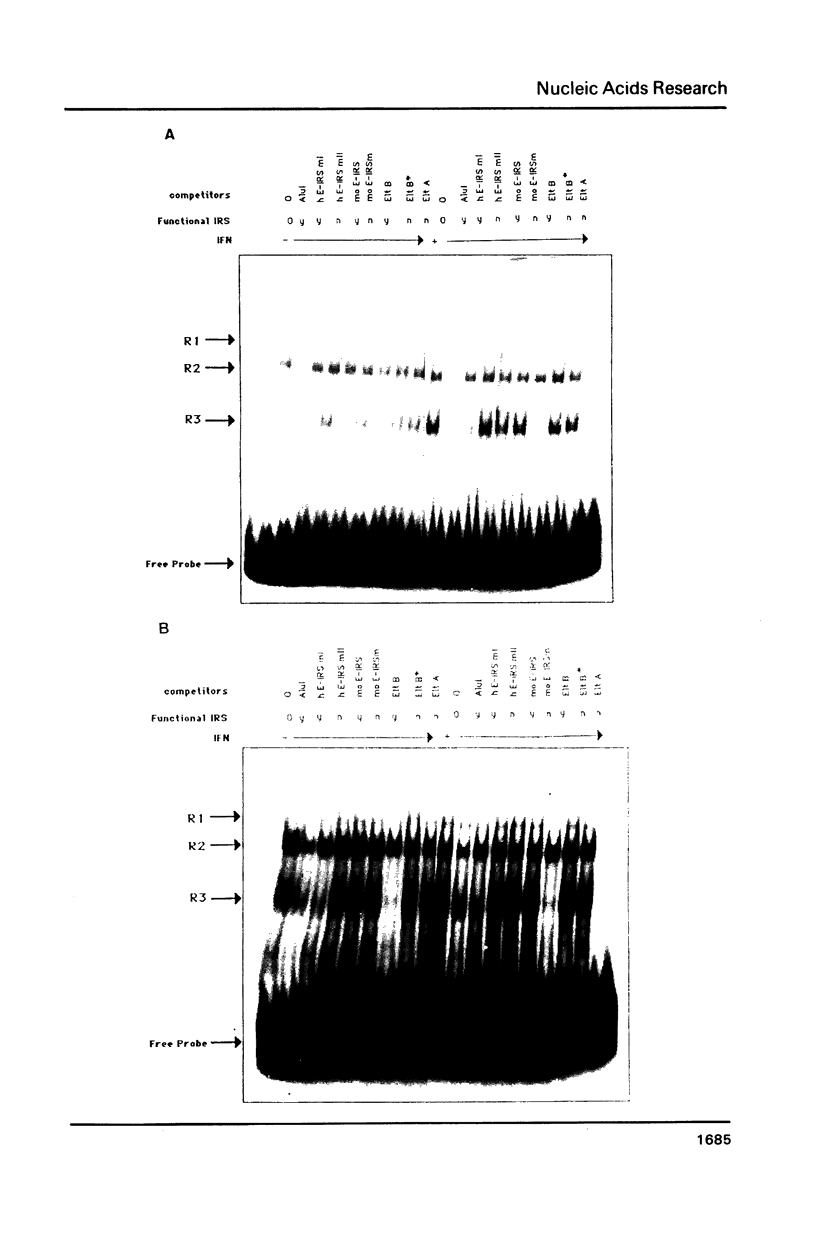
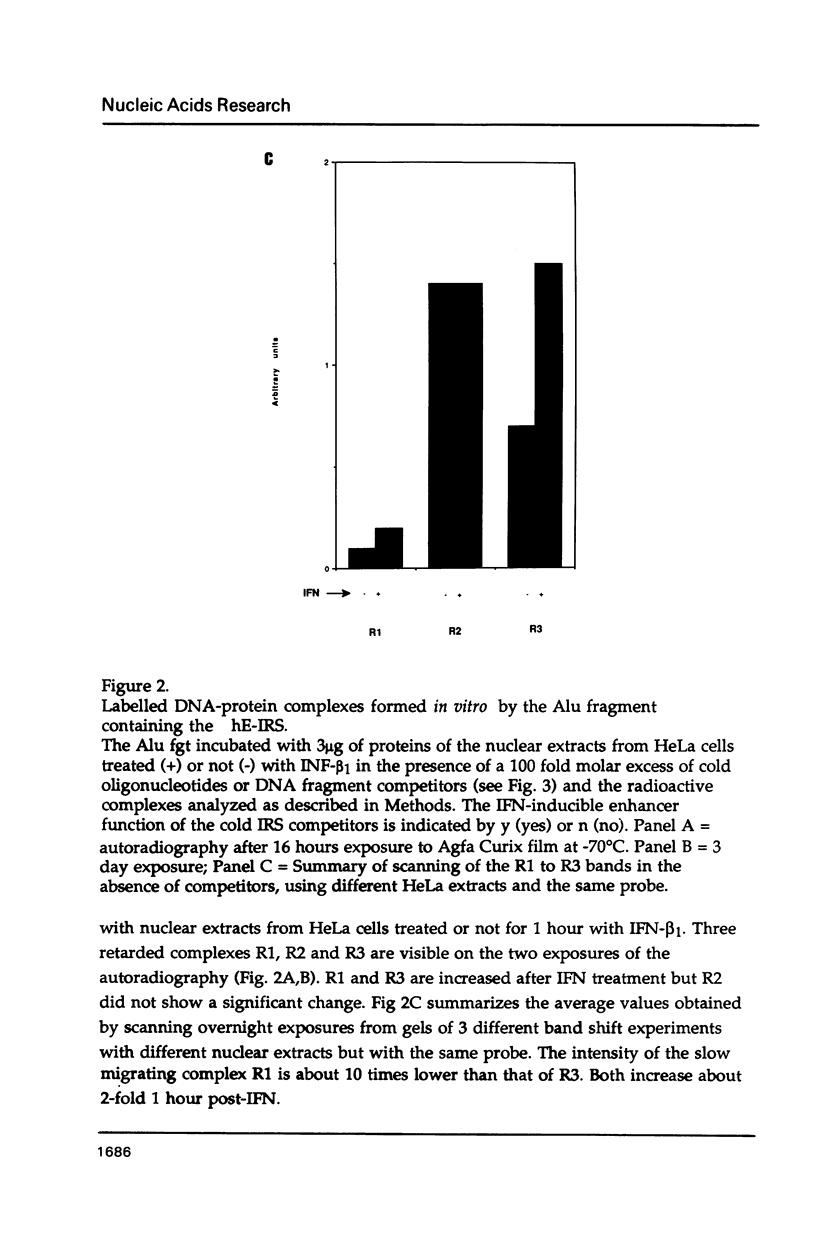
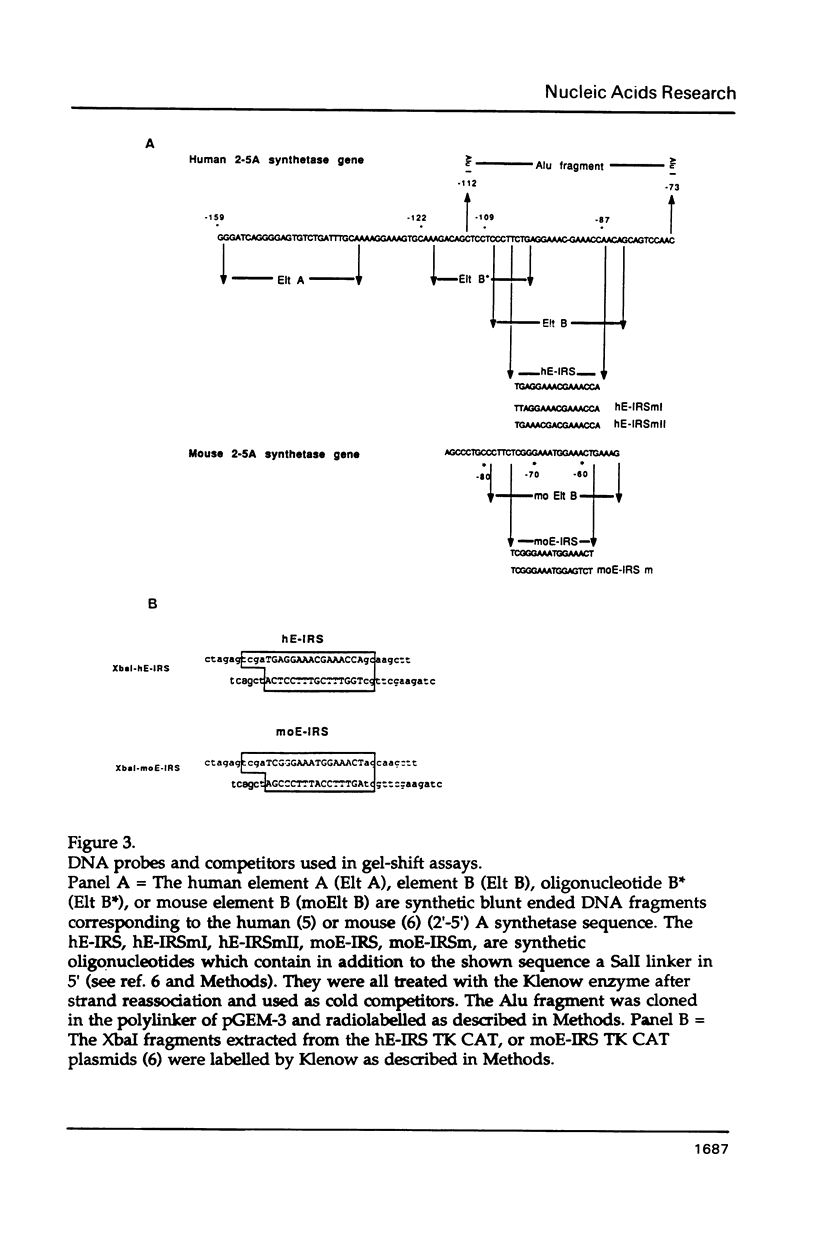
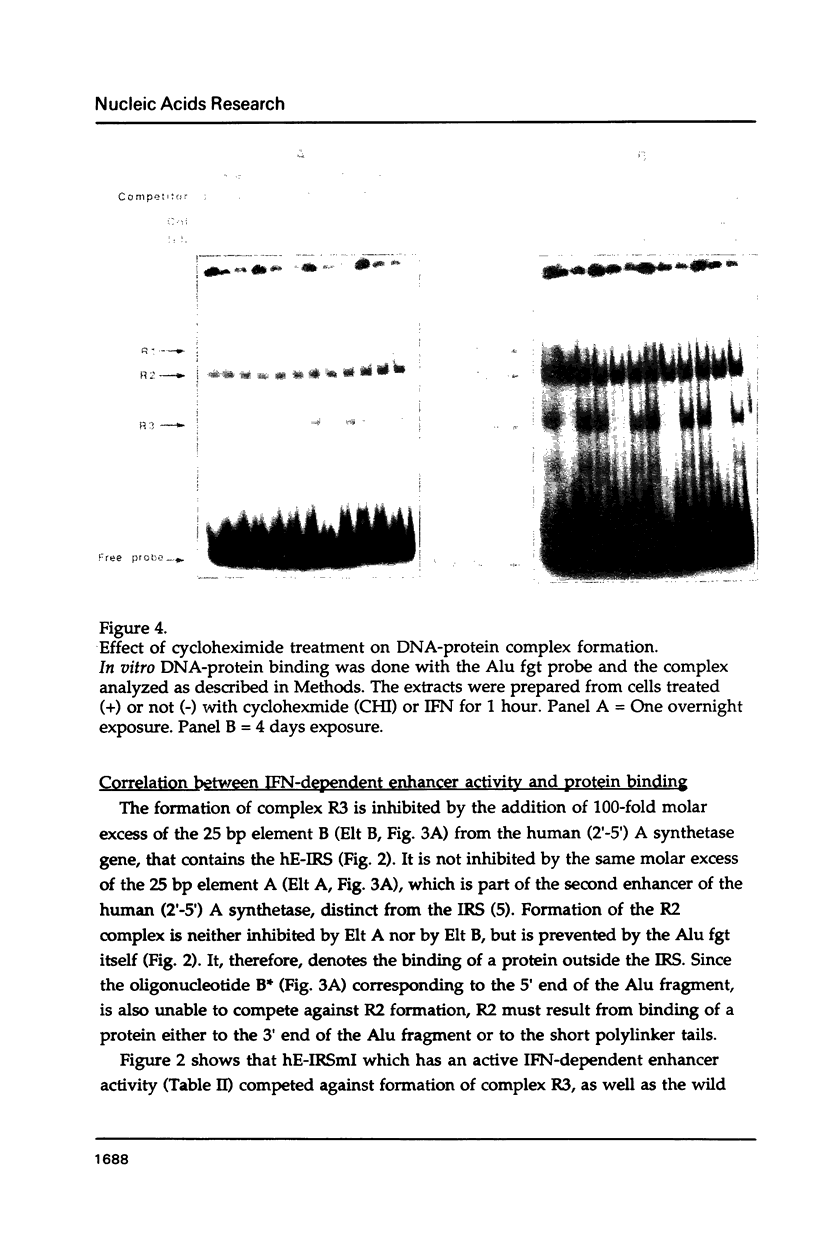
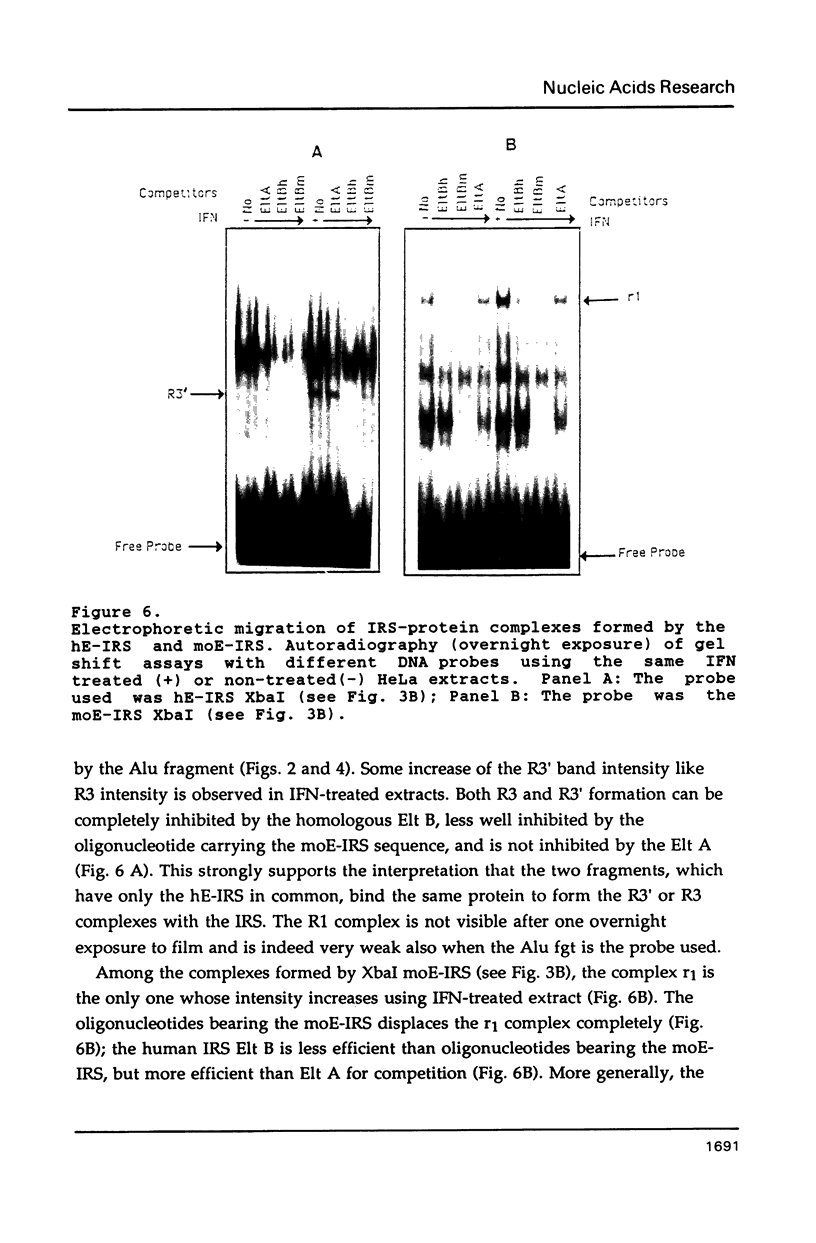
Mutants of the Interferon responsive sequence (IRS) of the mouse and human (2'-5') A synthetase (moE-IRS and hE-IRS) were tested for their Interferon (IFN)-inducible enhancer functions and for protein binding in vitro. Two complexes R1 and R3, were formed specifically with the hE-IRS. R3 migrated much faster and was about ten times more abundant than R1. R1 and R3 are increased about 2-fold in IFN-treated HeLa extracts relatively to extracts from non-treated cells. R1 and R3 seem to involve the same DNA sequence in the probe since they react identically to competitors. Two proteins of 69 and 46 kDa form the IRS specific complexes as revealed by UV cross-linking. Identical DNA probes bearing either the hE-IRS or moE-IRS form complexes of different characteristics with nuclear proteins, suggesting that the two IRS variants are the targets of binding of different proteins or of different protein complexes.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benech P., Vigneron M., Peretz D., Revel M., Chebath J. Interferon-responsive regulatory elements in the promoter of the human 2',5'-oligo(A) synthetase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4498–4504. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernajovsky Y., Mory Y., Chen L., Marks Z., Novick D., Rubinstein M., Revel M. Efficient constitutive production of human fibroblast interferon by hamster cells transformed with the IFN-beta 1 gene fused to an SV40 early promoter. DNA. 1984 Aug;3(4):297–308. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. A single polypeptide possesses the binding and transcription activities of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4723–4733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. A genetic approach to promoter recognition during trans induction of viral gene expression. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):53–59. doi: 10.1126/science.3018926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faltynek C. R., McCandless S., Chebath J., Baglioni C. Different mechanisms for activation of gene transcription by interferons alpha and gamma. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90315-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Manly S. P., McMahon M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferon-induced gene expression in human cells. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):745–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Stark G. R. alpha-Interferon-induced transcription of HLA and metallothionein genes containing homologous upstream sequences. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):637–639. doi: 10.1038/314637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannigan G., Williams B. R. Transcriptional regulation of interferon-responsive genes is closely linked to interferon receptor occupancy. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1607–1613. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04403.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug H., Costas M., Staeheli P., Aebi M., Weissmann C. Organization of the murine Mx gene and characterization of its interferon- and virus-inducible promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3065–3079. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel A., Kimura A., Fournier A., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. Interferon response sequence potentiates activity of an enhancer in the promoter region of a mouse H-2 gene. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):743–746. doi: 10.1038/322743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korber B., Mermod N., Hood L., Stroynowski I. Regulation of gene expression by interferons: control of H-2 promoter responses. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1302–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.3125612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusari J., Sen G. C. Transcriptional analyses of interferon-inducible mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):528–531. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., Chaudhuri A., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional induction by interferon. New protein(s) determine the extent and length of the induction. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):453–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luster A. D., Ravetch J. V. Genomic characterization of a gamma-interferon-inducible gene (IP-10) and identification of an interferon-inducible hypersensitive site. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3723–3731. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon M., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon-induced gene expression in wild-type and interferon-resistant human lymphoblastoid (Daudi) cells. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):362–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.362-366.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N., Evans B., Levy D., Fahey D., Knight E., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced transcription of a gene encoding a 15-kDa protein depends on an upstream enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6394–6398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford M. N., Hannigan G. E., Williams B. R. Interferon-induced binding of nuclear factors to promoter elements of the 2-5A synthetase gene. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):751–759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02872.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirayoshi Y., Burke P. A., Appella E., Ozato K. Interferon-induced transcription of a major histocompatibility class I gene accompanies binding of inducible nuclear factors to the interferon consensus sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5884–5888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari R. K., Kusari J., Sen G. C. Functional equivalents of interferon-mediated signals needed for induction of an mRNA can be generated by double-stranded RNA and growth factors. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3373–3378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. C., Morley B. J., Campbell R. D. Cell-specific expression of the human complement protein factor B gene: evidence for the role of two distinct 5'-flanking elements. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):331–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]