Fig 1.
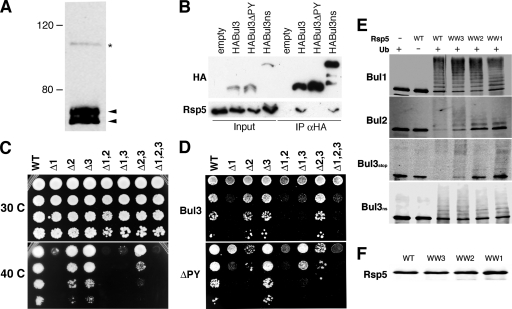
BUL genes are not essential for viability but are important for response to heat stress. (A) HA epitope-tagged Bul3p was expressed in a bul3Δ null mutant strain, and the protein was visualized by immunoblotting using anti-HA antibodies. The arrowheads indicate two major translation products of 55 to 60 kDa; the asterisk indicates a readthrough translation product of ∼100 kDa. (B) HABul3p was expressed in a bul3Δ strain, along with a Y100A (HABul3ΔPY) form, a variant that lacks the internal stop codon (HABul3ns), and an empty HA vector control. Extracts from log-phase cells (Input) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HA affinity resin (IP αHA) and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-HA and anti-Rsp5 antibodies. (C) Tenfold serial dilution of yeast strains with the BUL genes deleted alone (Δ1, Δ2, and Δ3), in pairs (Δ1,2; Δ1,3; and Δ2,3), or in combination (Δ1,2,3) were grown for 3 days at either 30°C or 42°C. WT, wild type. (D) Serial deletions as described for panel C with strains expressing HABul3 or HABul3ΔPY constructs. (E and F) In vitro ubiquitination assays using recombinant S-tagged Bul1p and Bul2p and large (Bul3ns) and small (Bul3stop) forms of Bul3p. The reactions were performed with methylated ubiquitin (Ub) using equal quantities, as determined using immunoblots with anti-Rsp5p antibodies (F), of wild-type Rsp5p and variants that had only a single functional WW domain remaining (WW3, WW2, and WW1) before being subjected to immunoblotting with anti-S-tag antibodies.