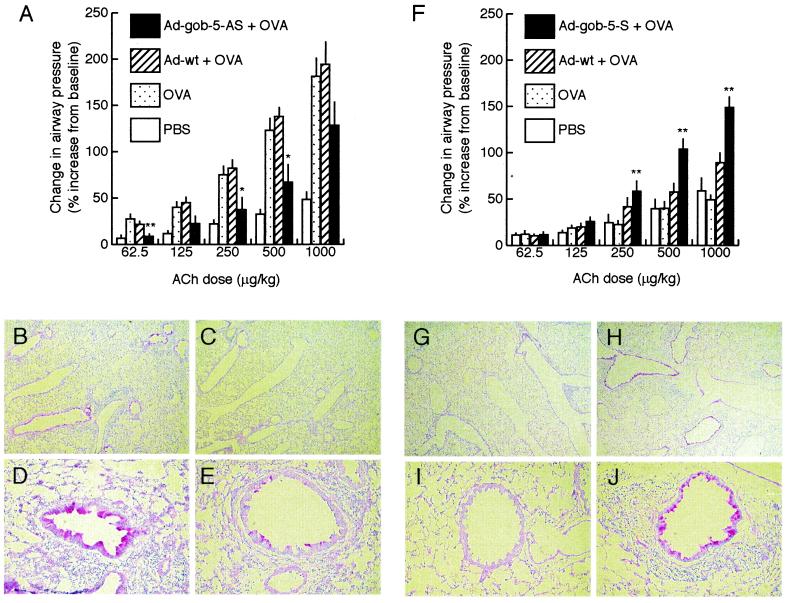
Figure 3.
Functional analysis of gob-5 in the development of AHR and mucus production by in vivo adenoviral gene transfer. (A) Reduction in airway responsiveness by the administration of adenovirus-expressing gob-5 antisense RNA in AHR-model mice (n = 5–10). Recombinant adenovirus-expressing gob-5 antisense RNA transcripts (Ad-gob-5-AS) and control adenovirus (Ad-wt) were intratracheally administered one day before the start of OVA inhalation. Airway responsiveness was measured 24 h after the final inhalation carried out for 6 consecutive days. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, compared with the OVA-inhaled group by Dunnett type test. (B–E) Suppression of airway mucus secretion by the administration of adenovirus-expressing gob-5 antisense RNA in AHR-model mice. Lung sections of Ad-wt-administered mice (B and D) and Ad-gob-5-AS-administered mice (C and E) were stained with PAS, counterstained with hematoxylin. Original magnifications, ×40 (B and C), ×200 (D and E). (F) Promotion of airway responsiveness by overexpressing gob-5 in OVA-inhaled mice (n = 6–10). Recombinant adenovirus expressing gob-5 RNA transcripts (Ad-gob-5-S) and control adenovirus (Ad-wt) were intratracheally administered 1 day before the start of OVA inhalation. Airway reactivity was measured 24 h after the final inhalation carried out for 3 consecutive days. **, P < 0.01, compared with OVA-inhaled group by Dunnett type test. (G–J) Induction of airway mucus secretion by overexpressing gob-5. Lung sections of Ad-wt-administered mice (G and I) and Ad-gob-5-S-administered mice (H and J) were stained with PAS, counterstained with hematoxylin. Original magnifications, ×40 (G and H), ×200 (I and J).