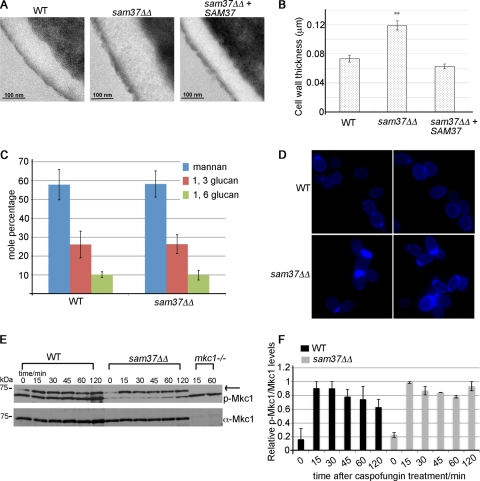
Fig 2.
Sam37 affects cell wall integrity in C. albicans. (A) Transmission electron microscopy showed thicker cell walls in the sam37ΔΔ mutant compared to the wild type and the reconstituted strain. (B) The thickness of the wall was measured for at least 10 individual cells from each of the strains, at three different positions on the cells. Shown are the averages of the measurements and the standard error. (C) The carbohydrate composition of the wall was measured by GC-MS. Shown is the mole percentage average from four or five replicates analyzed over two experiments and the standard deviation. (D) Equal numbers of cells from overnight cultures from the wild type and sam37ΔΔ mutant strains were stained with 250 μg/ml calcofluor white and visualized with fluorescence microscopy using the DAPI filter. Shown are composite pictures from 2 different fields for the mutant and the wild type, respectively. The original micrographs, including bright-field pictures of the same fields, are presented in Fig. S5 in the supplemental material. (E) Cells from the indicated strains were grown to log phase and then treated with 125 ng/ml caspofungin for the indicated times. Whole-cell protein extracts were prepared and proteins separated by SDS-PAGE. Phopsho-Mkc1 was detected using the anti-phospho Erk antibody (p-44/42). Mkc1 was detected by antibodies raised against the protein. (F) Quantification of the phospho-Mkc1 versus total Mkc1 bands was performed using ImageQuant. The highest phospho-Mkc1/total Mkc1 ratio in the wild type or the sam37ΔΔ mutant, respectively, was set to 1, and the other ratios were expressed relative to that. Equivalent results were obtained in several experiments. Shown are the averages of two independent experiments and the standard error.