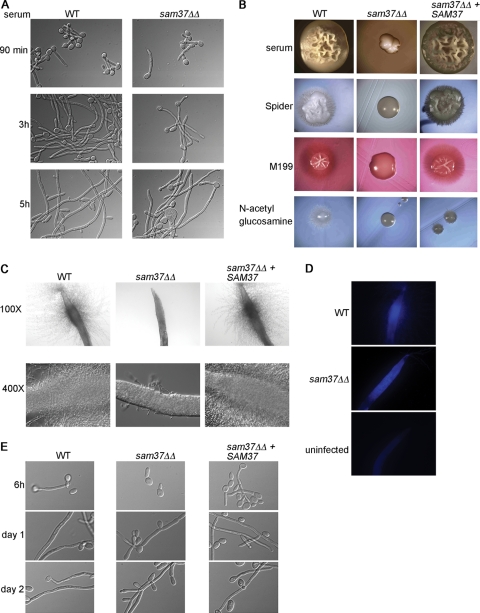
Fig 3.
Filamentous growth phenotypes of the C. albicans sam37ΔΔ mutant. (A) Filamentous growth in vitro was tested in 10% serum medium at 37°C. (B) Filamentation on solid medium was assessed by streaking out the wild type, sam37ΔΔ mutant or the complemented strain on the indicated plates and incubating at 37°C. Colonies from the wild type and the complemented strain on all media and the sam37ΔΔ mutant on serum plates were photographed at 20× magnification. The mutant colonies on Spider, M199, and N-acetylglucosamine-containing media were photographed at 60X magnification due to a much smaller size of the colony. (C) The worm C. elegans was infected with wild type C. albicans, the sam37ΔΔ mutant or the complemented strain and penetrative filamentation was monitored over time. The mutant only ever formed short and very few filaments. (D) Calcofluor white staining performed at day 5 of the infection showed that mutant cells were ingested by the worm. (E) Filamentation was assessed in vitro by microscopy, using growth medium equivalent to the worm assay (20% BHI in M9 buffer), at 37°C. In this medium, filaments were not visible in the wild type at 90 min or 3 h, and appeared only at the 6-h time point. The full time course is shown in Fig. S3B in the supplemental material.