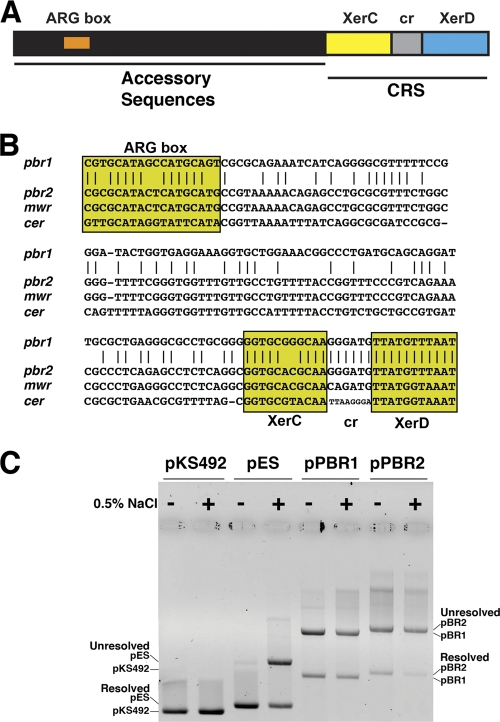
Fig 3.
(A) Schematic diagram of plasmid's Xer recombination sites. The sites contain a core recombination region that includes the 11-bp XerC and XerD binding sites and a central region (6 to 8 bp),and accessory sequences (180 bp) with which the architectural proteins ArgR and PepA interact. The diagram is not drawn to scale. (B) Comparison of the nucleotide sequences of pbr1 (present in pPAB19-1 and pPAB19-4), pbr2 (present in pPAB19-2 and pPAB19-3), mwr, and cer. The ArgR-binding site (ARG box) and different regions of the core recombination site (CRS) are shown. XerC, XerC-binding site; XerD, XerD-binding site; cr, central region. Identical nucleotides between pbr1 and pbr2 are indicated by vertical lines. (C) Dimer resolution assay. Dimers of plasmids pKS492 (cer), pES (mwr), pPBR1 (pbr1), and pPBR2 (pbr2) were introduced by transformation into E. coli DS941. The cells were cultured in medium containing 0 or 0.5% added NaCl in the presence of 100 μg of ampicillin per ml for 20 generations. Plasmid DNA was isolated and subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis. The positions of dimers and monomers are indicated at the sides.