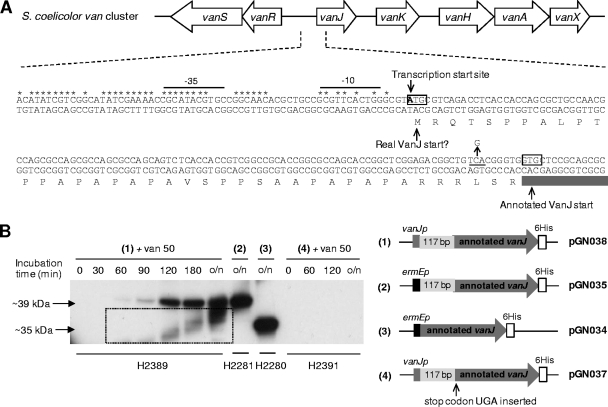
Fig 4.
(A) Genetic organization of the vancomycin resistance cluster in S. coelicolor showing details of the nucleotide sequence and annotation of the 5′ end of vanJ and its upstream region. Nucleotides in the conserved van promoter region are marked with asterisks, and the putative −35 and −10 sequences are indicated. The transcription start site (23) is shown, together with the annotated and alternative VanJ translational start codons. Amino acids encoded only from the alternative (most upstream) start codon are shaded in light gray, and the C-to-G mutation introducing a TGA translational stop codon between the two initiator codons is indicated with an arrow. (B) VanJ is expressed only from the upstream alternative start codon and is encoded by a leaderless message. His-tagged VanJ proteins expressed in the ΔvanJ null mutant strain using the plasmids illustrated were detected by immunoblot analysis with an anti-His antibody. For strains carrying pGN037 or pGN038, proteins were extracted from samples taken immediately before (0 min) and at the indicated times after the induction of expression by treatment with 50 μg/ml vancomycin. o/n indicates cultures were incubated overnight (approximately 18 h). Bands appearing in the box are an artifact arising from the exposure of the film.