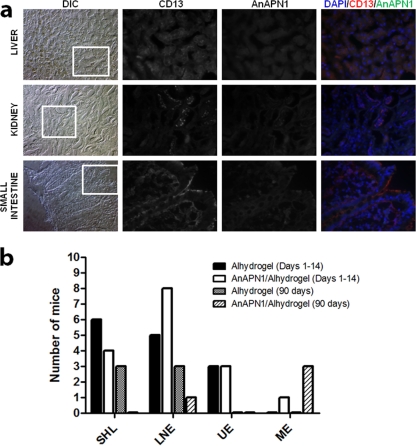
Fig 3.
An immunohistochemical study of normal human tissue sections with rabbit anti-AnAPN1 IgG and a complete histopathological analysis of mice following AnAPN1-Alhydrogel immunizations demonstrated the complete absence of cross-specific staining of human APN homologs and gross histopathologies in mice. (a) Frozen sections were stained with anti-CD13, MAb (WM15 clone, positive control), and polyclonal rabbit anti-AnAPN1 IgG and detected with anti-mouse Texas Red and anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated antibody. Images were acquired at 200× and 400× magnifications. Differential interference contrast (DIC) images are provided for orientation at 200×, and the inset corresponds to the anti-CD13 and anti-AnAPN1 staining and the merged image, which were all acquired at 400×. DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) was used to stain nuclei and appear blue. The signal observed in the 460- to 490-nm band pass filter range across all AnAPN1 images corresponds to the marked autofluorescence observed for these tissues. (b) A summary of the acute (days 1 to 14) and chronic (90 days) histopathology results in control (Alhydrogel) and treatment (AnAPN1-Alhydrogel) mouse cohorts A and B (see the Fig. 2 legend), respectively. SHL, small hepatic lesions; LNE, lymph node enlargements; UE, urinary tract edema; ME, mild enteritis.