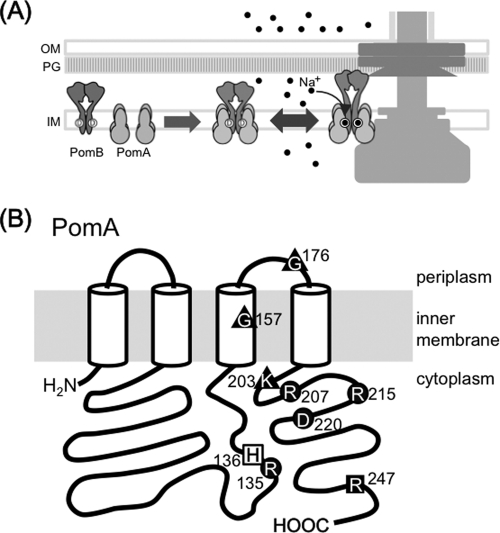
Fig 1.
Diagram of the flagellar motor and the stator component PomA. (A) A schematic model of the stator assembly around the rotor in the Na+-driven flagellar motor of the polar flagellum in V. alginolyticus. The circles with the letter D inside indicate the Na+ binding sites of PomB. The black dots represent sodium ions. OM, outer membrane; PG, peptidoglycan layer; IM, inner membrane. (B) PomA point mutations studied in this report were mapped on a schematic diagram and are indicated as black circles with residue numbers. ■, mutation disrupts PomA protein expression; ▲, mutations disrupt PomA/B complex formation; ●, mutations disrupt ion conduction; □, mutation keeps both PomA/B complex-forming ability and ion conductivity. All of these mutations show a nonmotile phenotype except for R207E, which is slow-motile, and reduced stator polar localization rates, around 30% or less, whereas the wild type shows a rate reduction of more than 80%.