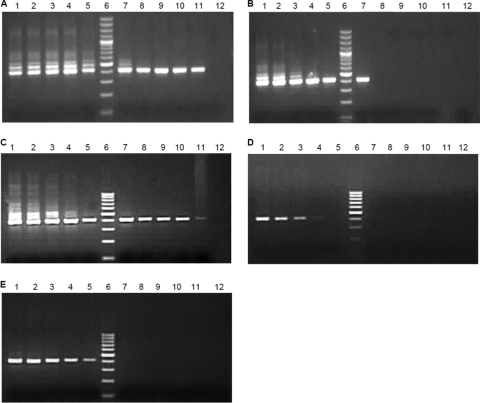
Fig 3.
Specificity and sensitivity of the strand-specific assays. Synthetic positive-sense and negative-sense RNAs were diluted 10-fold, and RNA copies ranging from 1010 to 10 were subjected to strand-specific PCR separately. The cDNAs were synthesized in the presence of 1 μg of total cellular RNA with Superscript RT-III and treated with exonuclease I (where mentioned) for 30 min followed by silica-based column purification. A 10-μl volume of cDNA was used for the first round of PCR, and 5 μl of the first PCR product was further subjected to nested PCR. Lanes in all four gels represent the following: 1, 1010 RNA copies; 2, 109 RNA copies; 3, 108 RNA copies; 4, 107 RNA copies; 5, 106 RNA copies; 6, 100-bp ladder; 7, 105 RNA copies; 8, 104 RNA copies; 9, 103 RNA copies; 10, 102 RNA copies; 11, 10 RNA copies; 12, no RNA. (A) Positive-strand assay on synthetic positive strand with exonuclease. (B) Positive-strand assay on synthetic negative strand with exonuclease. (C) Negative-strand assay on synthetic negative strand with exonuclease. (D) Negative-strand assay on synthetic positive strand with exonuclease. (E) Negative-strand assay on synthetic positive strand without exonuclease.