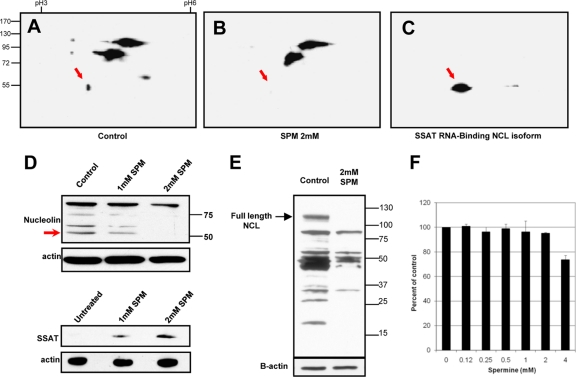
Fig 6.
Exogenous spermine reduces 55-kDa nucleolin isoform. 2D Western blots in panels A, B, and C used IPG strips (pI 3 to 6) for the first separation, SDS-PAGE for the second, and monoclonal antinucleolin antibody for the blots. Red arrows point to the position of the 55-kDa isoform that binds to the SSAT-RNA column and is missing or reduced in cells exposed to spermine. (A) HEK293T cells grown under control conditions. (B) HEK293T cells exposed to 2 mM spermine for 12 h. (C) Proteins eluted from a SSAT-RNA interaction column (high intensity of the 55-kDa spot results from column enrichment). (D) Western blots of cells exposed to 0, 1, and 2 mM spermine for 12 h. Upper and lower blots are from the same 3 cultures: upper panels show dose-dependent spermine-induced degradation of the 55-kDa nucleolin isoform, and lower panels show corresponding spermine-induced increases in the SSAT protein. (E) Polyamine-mediated nucleolin degradation by 48 h of spermine exposure. (F) An Alamar blue assay was used to test viability of HEK293T cells grown for 48 h in the indicated spermine concentrations. Aminoguanidine (1 mM) was included in all cultures to inhibit generation of reactive oxygen species by amine oxidase activity of serum in the media.