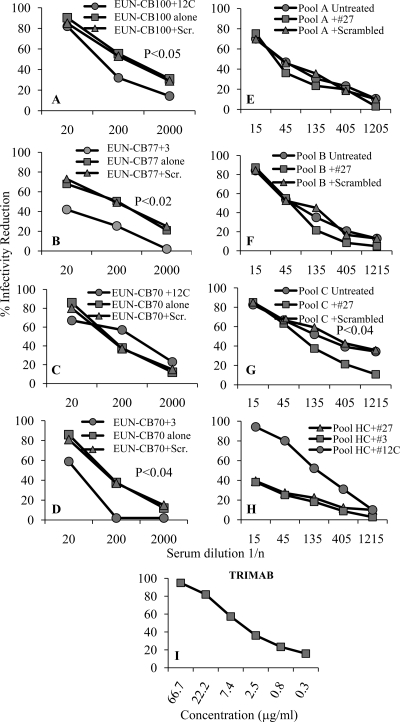
Fig 4.
Neutralization specificity of anti-HIV antibodies from single or pooled cord blood serum samples. All neutralization assays were performed on the DU156 HIV isolate (C-R5) with cord blood specimens from EUN babies; statistical significance (two-tailed t test) is indicated in each panel. Both controls and cord blood samples were tested in three replicates. (A) CB100 preadsorbed with scrambled and 12-C peptides; (B) CB77 preadsorbed with scrambled peptide and peptide 3; (C) CB70 preadsorbed with scrambled peptide and peptide 12-C; (D) CB70 preadsorbed with scrambled peptide and peptide 3; (E) pool A (five random, ELISA-negative samples) preadsorbed with scrambled peptides and peptide 27; (F) pool B (five random, ELISA-positive samples) preadsorbed with scrambled peptides and peptide 27; (G) pool C (five random, ELISA-positive samples) preadsorbed with scrambled peptide and peptide 27; (H) pool of CB serum from 5 HIV-uninfected babies preadsorbed with scrambled peptide and peptides 3, 12-C, and 27; (I) TriMab neutralization control. The x axis from panels A to H report serum dilution as 1/n, panel I reports concentrations of TriMab. Peptide sequences are given in Table 1. Scr., scrambled.