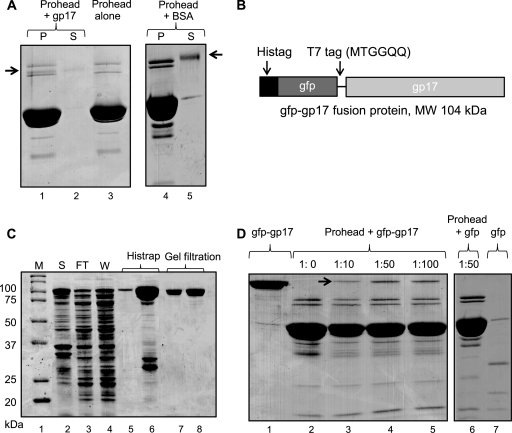
Fig 2.
gp17 binds to prohead. Binding assays were performed according to the procedure described in Materials and Methods. (A) Proheads (30 nM; 2 × 1011 particles) were incubated either alone (lane 3) or with gp17-K577 (lane 1) or BSA (lane 4). Lanes 2 and 5 show unbound K577 and BSA, respectively, in the supernatant fraction. (B) Schematic of the gfp-gp17 fusion construct. The gfp sequence (44) was fused to the N terminus of gp17 with a T7 tag as a linker in between. (C) Overexpression and purification of gfp-gp17. The E. coli lysate (lane 2) was applied to the Histrap column. Lanes 3 and 4 show flowthrough and wash fractions, respectively. The gfp-gp17 fractions eluted with imidazole (lanes 5 and 6) were pooled together and applied to Superdex-200 size exclusion column. The peak gfp-gp17 fractions (lanes 7 and 8) were collected and used for binding assays. Molecular mass markers (M) are shown in lane 1. (D) Binding of gfp-gp17 to proheads. Proheads (2 × 1011) were incubated with increasing ratios of gfp-gp17 to gp20 (lanes 2 to 5) or gfp at ratio of 1:50 to gp20. Lanes 1 and 7 show unbound gfp-gp17 and gfp, respectively.