Fig 3.
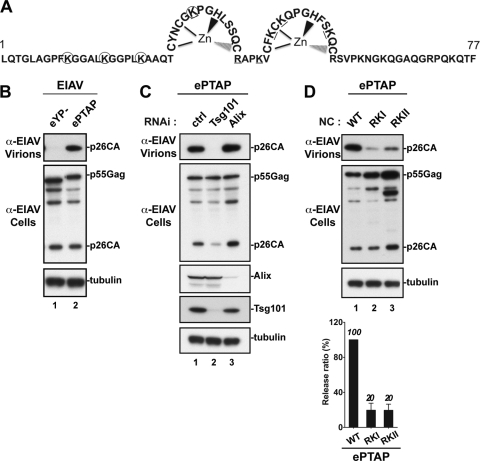
NC is required for virus release when PTAP is inserted into a heterologous Gag protein. (A) Schematic representation of the EIAV NC domain (amino acids 1 to 77). Lysine (K) and arginine (R) residues replaced with alanine in the ePTAP-RKI and ePTAP-RKII mutants are circled and underlined, respectively. (B) 293T cells were transfected with L domain mutant EIAV (eYP−) or EIAV carrying PTAP as the L domain (ePTAP). Pelleted virion and cell lysate were analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. (C) Depletion of Tsg101 or Alix in 293T cells and its effect on viral release. 293T cells were cotransfected as described in Materials and Methods, with ePTAP and control RNAi (ctrl, lane 1) or Tsg101 (lane 2)- or Alix (lane 3)-specific RNAi. Pelleted virion and cell lysate fractions were analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. (D) Effects of NC mutations on EIAV release mediated exclusively via the PTAP L domain. 293T cells were transfected with ePTAP carrying a WT or mutated NC. Pelleted virion and cell lysate fractions were analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. Relative virus release efficiencies are shown at the bottom (± the standard deviations; n = 3).