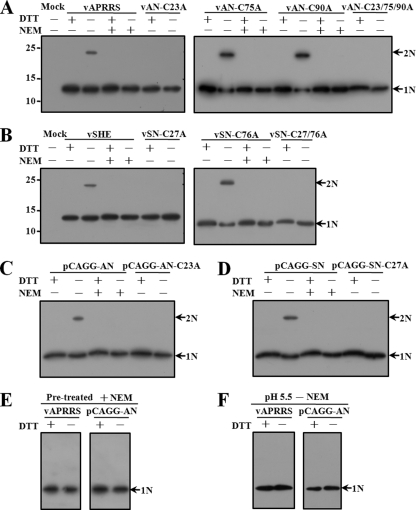
Fig 5.
Dimerization of cellular N proteins. Virus-infected or expression vector pCAGGS-transfected cells were lysed in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 1 mM NEM, separated by SDS-PAGE under reducing (+DTT) or nonreducing (−DTT) conditions, and subjected to Western blot analysis. (A) N proteins expressed from wild-type and mutant type II PRRSV APRRS. (B) N proteins expressed from wild-type and mutant type I PRRSV SHE. (C) Wild-type and cysteine mutant APRRS N proteins expressed from the mammalian vector pCAGGS. (D) Wild-type and cysteine mutant SHE N proteins expressed from pCAGGS. (E) Cellular APRRS N proteins expressed from virus or pCAGGS were treated with 1 mM NEM before cell lysis. Cells then were lysed without NEM and subjected to SDS-PAGE under reducing or nonreducing conditions, followed by Western blotting. (F) Cellular APRRS N proteins expressed from virus or pCAGGS were lysed at pH 5.5 without NEM treatment. Cell lysates then were subjected to SDS-PAGE under reducing or nonreducing conditions and analyzed by Western blotting. Monomers (N) or dimers (2N) of the N protein are indicated by arrows.