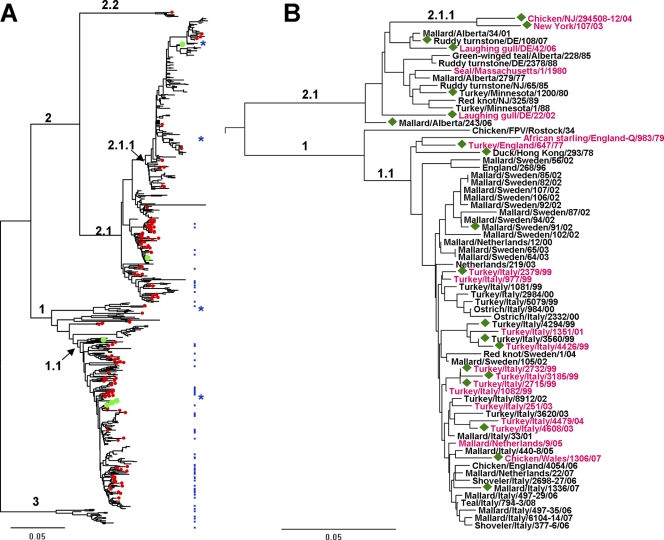
Fig 1.
Evolutionary relationships of H7 HAs. Phylogenetic trees for the amino acid sequences of the HA1 protein were inferred by the neighbor-joining method using MEGA software version 5 (61). The scale bars represent 0.05 units of amino acid substitutions per site. (A) The tree is based on 665 sequences available from GenBank and 19 sequences determined in this study. Numbered branches include viruses from the Eastern Hemisphere (clade 1) and the Western Hemisphere (clade 2); viruses from North America (clade 2.1) and South America (clade 2.2); viruses isolated in Europe and Asia after 1970 (clade 1.1); North American poultry influenza viruses with an eight-amino-acid deletion in the receptor-binding site (clade 2.1.1); and H7 equine influenza viruses (clade 3). Red dots mark viruses isolated from wild and domestic aquatic birds (mainly ducks). Green dots mark viruses isolated from humans. Blue dots depict viruses tested for receptor binding properties in this study; blue stars show four viruses characterized previously (20). (B) Tree for the viruses tested in this study and in reference 20. The strain names are colored in accord with the viral receptor-binding specificity: black, typical poultry-virus-like phenotype (Fig. 2B); purple, atypical poultry-virus-like phenotype (Fig. 2C). Green diamonds depict viruses that bind to 6′SLN. The numbering of the clades is the same as in panel A.