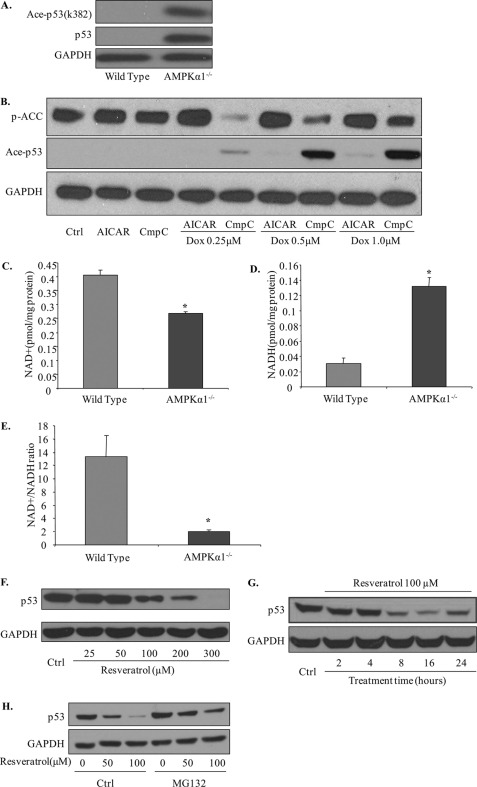
FIGURE 5.
Increased acetylation and decreased degradation of p53 in Ampkα1−/− MEFs due to defective SIRT1 activation. A, increased acetylation of p53 (Ace-p53) and total p53 levels in Ampkα1−/− MEFs compared with wild-type MEFs. B, inhibition of AMPK by compound C (CmpC) increased the doxorubicin (Dox)-induced acetylation of p53 in wild-type MEFs. C, intracellular NAD+ content (**, p < 0.01; n = 6 in each group). D, NADH levels in MEFs. E, calculated NAD+/NADH ratio (**, p < 0.01; n = 6 in each group). F, p53 protein levels after resveratrol treatment in Ampkα1-deficient MEFs for 16 h at the indicated dose. G, p53 protein levels after resveratrol treatment in Ampkα1−/− MEFs at 100 μm for indicated time points. H, MG132 blocks the effect of resveratrol in decreasing p53 levels in Ampkα1−/− MEFs. Ctrl, control; p-ACC, phospho-acetyl-CoA carboxylase; AICAR, 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleoside.