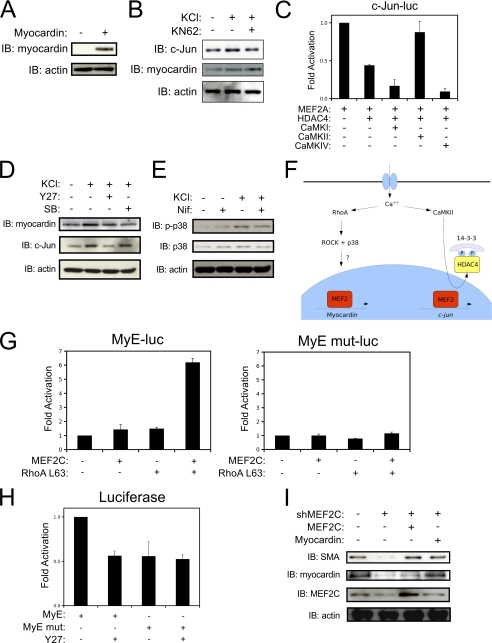
FIGURE 2.
Distinct calcium-mediated signaling pathways regulate myocardin and c-Jun expression in VSMCs. A, COS7 cells were transfected with Myocardin-856 and subjected to immunoblotting with myocardin antibody (SC-33766, Santa Cruz Biotechnology). B, A10 cells were treated with 60 mm KCl for 2 h following 15 min pretreatment with 5 μm KN-62 (CaM kinase inhibitor) or DMSO as a vehicle control. Protein extracts were immunoblotted with c-Jun, myocardin, and actin antibodies. C, A10 cells were transfected with a c-jun reporter-gene (c-Jun-luc), MEF2A, HDAC4, and activated CaMKI, CaMKII or CaMKIV, as indicated. D, A10 cells were pretreated with either Y27632 (Y27, 5 μm) or SB203580 (SB, 5 μm), or DMSO as a vehicle control for 15 min, then depolarized for two hours. Extracts were subjected to immunoblotting as indicated. E, A10 cells were pretreated with nifedipine, depolarized, and subjected to immunoblotting. F, model of the distinct signaling pathways that regulate MEF2-dependent myocardin and c-jun expression in VSMCs. G, A10 cells were transfected with MyE or the enhancer with the MEF2 site mutated (MyE mut) along with a MEF2C, and/or an active RhoA (RhoA L63) expression vectors. Extracts were subjected to luciferase assays. H, A10 cells were transfected as described in G, treated with Y27632 (Y27, 5 μm), and harvested for luciferase assay. I, cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding a short-hairpin RNA targeting MEF2C (shMEF2C), and expression vectors for human MEF2C or myocardin, as indicated. Cultures were enriched for expression of the shRNA by puromycin selection, and extracts were subjected to immunoblotting. Error bars indicate S.E.