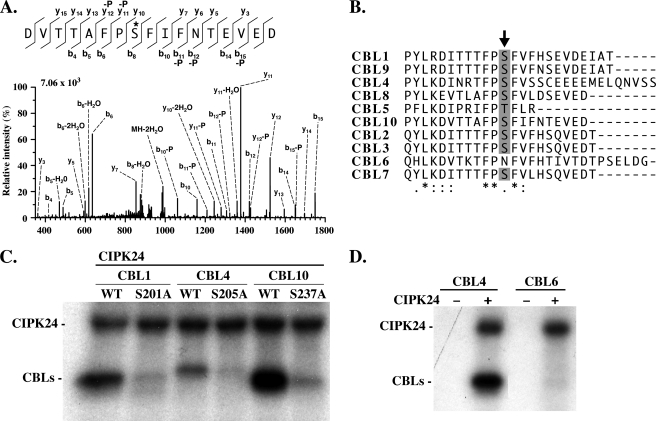
FIGURE 4.
The target site of CIPK-mediated phosphorylation is conserved in Arabidopsis CBL proteins. A, LC-multistage activation spectrum showing phosphorylation of CBL10 Ser237. Fragmentation of the precursor (m/z 1006.9353, doubly charged) was performed by collision-induced dissociation (CID). The major b-type and y-type ions as well as ions corresponding to the neutral loss of phosphoric acid (-P) are indicated in the spectrum and in the corresponding amino acid sequence depicted above the spectrum. The phosphorylation site is marked by an asterisk. The +80-Da mass shift observed for b8 to b15 and y10 to y15 in addition the occurrence of corresponding neutral loss ions revealed the phosphorylation of Ser237. B, ClustalW alignment of the Arabidopsis CBL C-terminal region. The conserved phosphorylation site is indicated by an arrow. Semi-conserved, conserved, and fully conserved amino acid residues are indicated by dots, double dots, and asterisks below the alignment, respectively. C, compared with CBL wild-type (WT) proteins, mutation of the corresponding phosphorylation site in CBL1 (Ser201), CBL4 (Ser205), and CBL10 (Ser237) to Ala prevented phosphorylation by CIPK24 in in vitro kinase assays. D, CIPK24 did not phosphorylate CBL6, which lacks the conserved Ser/Thr residue in the C terminus. Autoradiograph of in vitro phosphorylation assays in the absence (−) or presence (+) of CIPK24 with 50 ng of CBL4 (left) and CBL6 proteins (right). CBL4 as the positive control was phosphorylated by CIPK24.