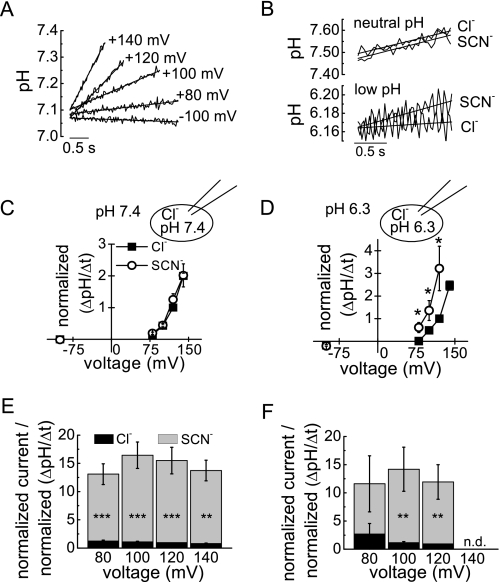
FIGURE 2.
Internal protons do not alter the uncoupling effect of external SCN−. A, representative recordings of time- and voltage-dependent internal alkalinization in a cell expressing ClC-5. Lines represent linear fits to the data. B, representative recordings of time-dependent ClC-5-mediated intracellular alkalinization at +120 mV at symmetric pH 7.4 (upper panel) and pH 6.3 (lower panel). C and D, rates of intracellular pH change in external Cl− and SCN− at symmetric pH 7.4 (C) and pH 6.3 (D) normalized to the value in Cl− at +120 mV. Rates were determined using the slope of the linear fits to the data, as shown in A. Averaged proton flux densities at +120 mV and symmetric pH 7.4 were 9.8 × 10−3 ± 1.3 × 10−3 ΔpH s−1 pF−1 for external Cl− (n = 17) and 10.2 × 10−3 ± 1.1 × 10−3 ΔpH s−1 pF−1 for SCN− (n = 14). The corresponding averaged proton flux densities at symmetric pH 6.3 were 1.9 × 10−3 ± 0.5 × 10−3 ΔpH s−1 pF−1 for external Cl− (n = 6) and 4.3 × 10−3 ± 1.0 × 10−3 ΔpH s−1 pF−1 for SCN− (n = 6). E and F, relative transport coupling of WT ClC-5 in external Cl− and SCN−. Currents were normalized to +120 mV in Cl− and divided by the normalized proton fluxes at the same voltage at symmetric pH 7.4 (E; n = 6–17) and symmetric pH 6.3 (F; n = 4–5). Asterisks indicate significant differences: ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05 (paired t test for non-normalized cells measured in both extracellular solutions at the same voltage). n.d., not determined.