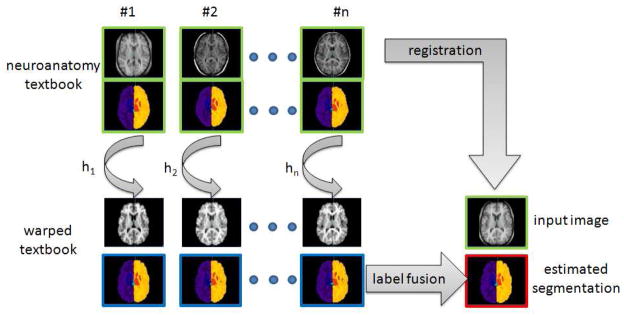
Fig. 1.
Principle of registration-based label propagation methods. The input data (shown with green borders) are an anatomy textbook (i.e. a set of N anatomical images with the corresponding label maps), and one anatomical image I. The set of anatomical images of the textbook is (non-linearly) registered to the input image I, and each label map is deformed with respect to the estimated transformation Hi. The final image segmentation (shown with red borders) is then obtained by fusing all the deformed label maps (shown with blue borders).