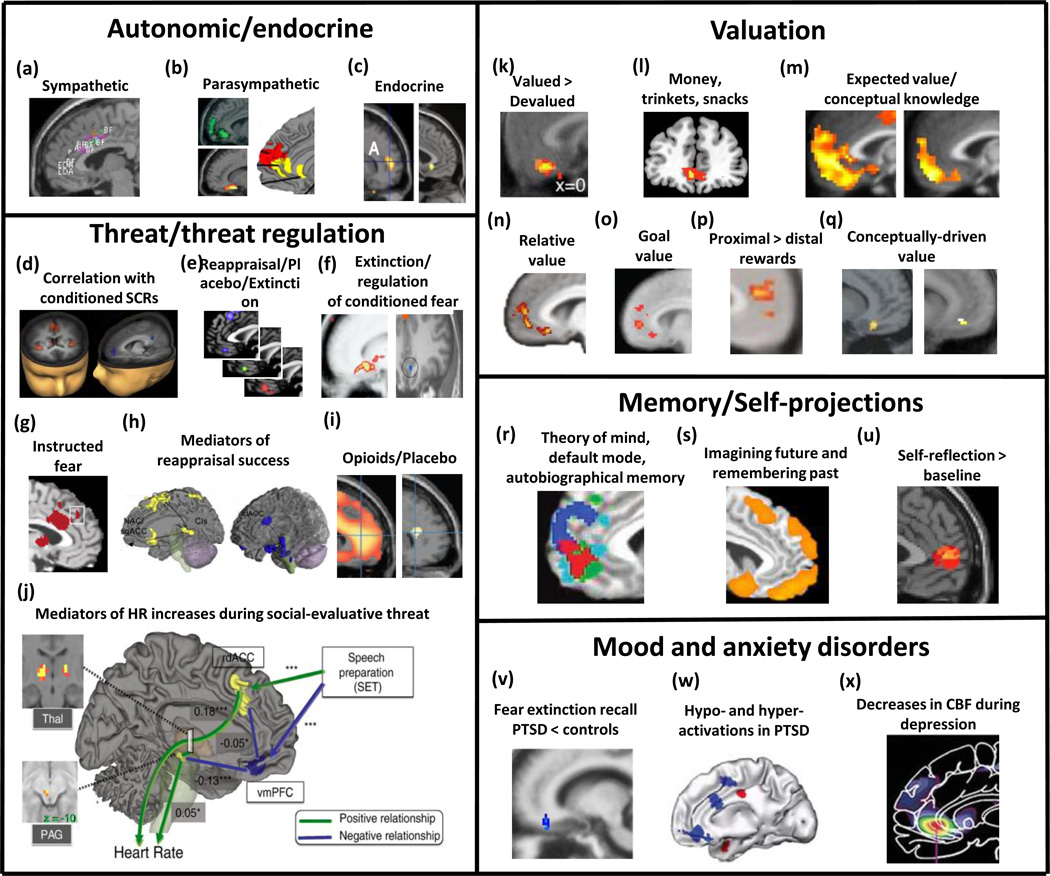
Figure 1.
Convergence across fields: VMPFC across social, cognitive, affective, and clinical domains. (a) Dorsal anterior/mid cingulate activations re sympathetic activity during emotional/cognitive tasks and exercise [1]. (b) pgACC, sgACC and rostral MPFC activity correlations with parasympathetic/anti-sympathetic activity; top-left: negative correlation with increases in heart rate during a working memory task [90]; bottom-left: decreases in skin conductance during relaxation [91]; right: results from a meta analysis on brain activations associated with high-frequency heart rate variability during emotional and cognitive tasks (red: emotional>cognitive; yellow: emotional = cognitive) [92] (c) left: Stress-related correlates of natural killer (NK) cells increase [93]; right: grief-evoking words correlates with IL-6 [94]. (d) vmPFC and rdACC activity negatively and positively correlates with conditioned SCR during fear conditioning and revearsal [4]; (e) vmPFC activation in meta-analyses of fear extinction (red), placebo (green) and reappraisal (blue). (f) left: vmPFC/sgACC activity during extinction recall [74]; right: vmPFC/sgACC activity (blue) during reappraisal of conditioned fear [52]. (g) rdACC activity in instructed fear paradigms [50]. (h) Positive (left: sgACC/Nacc) and negative (right: rdACC/amygdala) mediators of successful reappraisal of negative emotions [54] (i) left: opioids activate MPFC [95]; right: placebo activates a common sub-region in rACC [95]. (j) Positive (rdACC, thalamus, PAG) and negative (vmPFC) mediators of heart rate increases during social evaluative threat [65]. (k) vmPFC/mOFC activation for valued vs devalued food [46]. (l) Common coding of value of money, trinkets and snacks [67]. (m) left: integration of conceptual knowledge and value representations during decision-making; right: more rostral activity specific to explicit conceptual knowledge [78]. (n) Relative coding of value in the vmPFC [49]. (o) Goal value: healthiness of food for successful dieters or taste of food for unsuccessful dieters [73]. (p) temporal discounting of subjective value [72]. (q) left: same odor labeled as “cheddar cheese” vs “sweat” [68]; right: same wine labeled as “cheap” vs “pricey” [70]. (r) Convergence (red) of activations related to autobiographical memory (light blue), theory of mind (dark blue) and default-mode network (green) [96]. (s) Activity related to imagining past or future events or remembering past events [97]. (t) Activity related to self-reflection [98]. (u) Reduced activation during recall of extinction in PTSD patients vs controls [38]. (v) Hypo- (blue) and hyper- (red) activations in response to aversive stimuli in PTSD patients vs controls [10]. (w) Reduced cerebral blood flow (CBF) in depressed patients vs controls [79]. sgACC: subgenual anterior cingulate cortex, pgACC: perigenual anterior cingulate cortex, rACC: rostral ACC, rdACC: rostro-dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, MPFC: medial prefrontal cortex, vmPFC: ventromedial prefrontal cortex, mOFC: medial orbitofrontal cortex, Nacc: nucleus accumbens, PAG: periaqueductal gray matter SCR: skin conductance response, IL-6: interleukin -6.