Fig. 1.
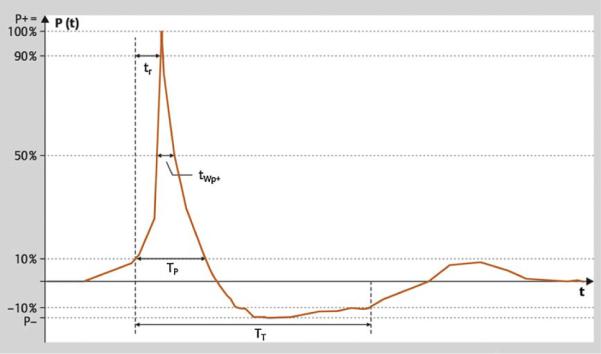
Typical shock wave pulse form in the focal zone. There is a rapid pressure increase at t0 to a peak pressure value P+, with the rise time tr followed by a decrease to zero crossing the zero line at t1 and a negative phase P− until t2. The time interval t0 to t1 is denominated a positive pulse duration tp+. P+ varies according to the intensity settings of the shock wave generator. The pulse width tw is defined as the time during which peak pressure is >50% of P+. The pressure profile P(x,y,z,t) describes shock waves in one specific location of the pressure field. The focal width is defined according to the −6-dB contour in the x and y direction.