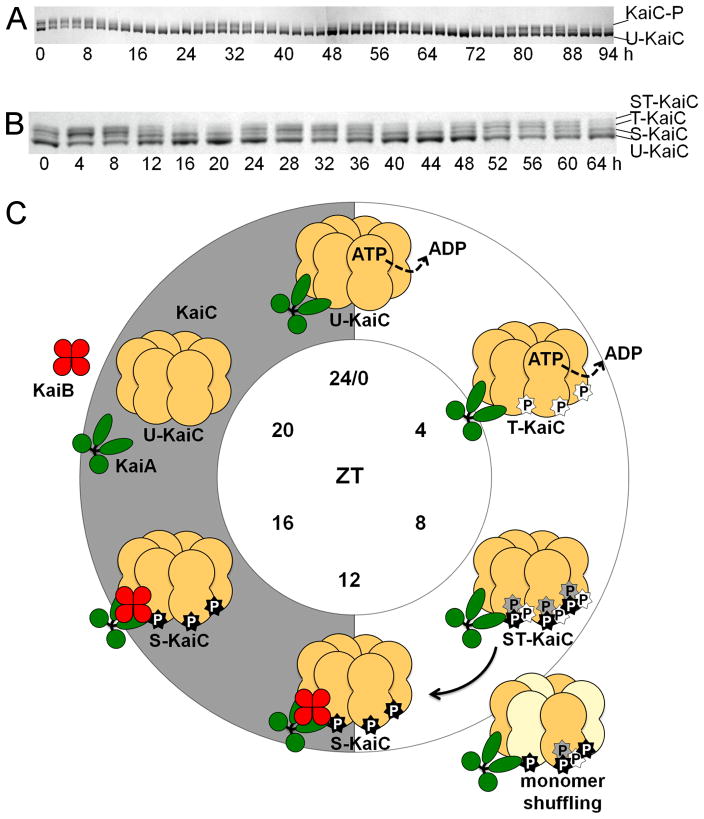
Figure 2.
In vitro KaiC-P oscillation and biochemical model for KaiC-P oscillatory activity. (A) In vitro oscillation of KaiC-P for 4 days taken at 2-h time points. U-KaiC, unphosphorylated KaiC; KaiC-P, phosphorylated KaiC. (B) In vitro KaiC-P oscillation with resolved phosphoforms. In vitro reactions were incubated for 3 days with samples taken at 4-h time points. Four phosphoforms of KaiC exist over the course of a phosphorylation cycle. ST -KaiC, S431 and T432 KaiC double phosphoform; T-KaiC, T432 KaiC phosphoform; S-KaiC, S431 KaiC phosphoform; and U-KaiC, unphosphorylated KaiC. Immunoblot images provided by Yong-Ick Kim, UC-San Diego. (C) Model for ordered phosphorylation and monomer shuffling activity in KaiC. Initially at ZT 0, unphosphorylated KaiC (U-KaiC) associates with KaiA to induce phosphorylation of KaiC (T-KaiC) at T432 (white star) at ZT 4, which is subsequently followed by phosphorylation at S431 (black star) and possibly T426 (gray star) for a fully phosphorylated KaiC (ST-KaiC) by ZT 8. Fully phosphorylated KaiC initiates the dephosphorylation stage and is amenable to monomer shuffling between ZT 8 and 12 to synchronize multiple intracellular KaiC hexamers, leading to the lone S431 phosphoform (S-KaiC) by ZT 12 and association with KaiB. KaiC continues autodephosphorylation through ZT 16, yielding U-KaiC by ZT 20. Note that indicated KaiC phosphoforms at each ZT time represent the most prominent KaiC-P phosphoform relative to the population. P, phosphate.