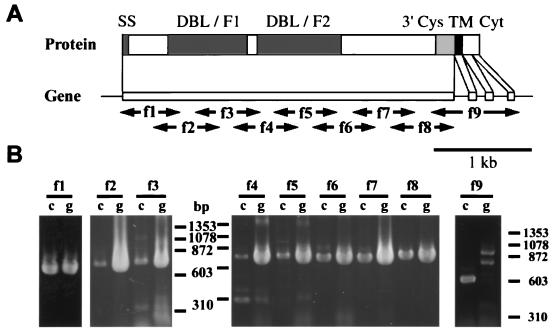
Figure 1.
Sequencing strategy and exon/intron structure of baebl. Oligonucleotides were designed based on the genomic sequence obtained from the P. falciparum genome project (Sanger Centre) and used for the sequencing of genomic DNA (GenBank Accession No. AF332918) and reverse transcription–PCR of mRNA (GenBank Accession No. AF332919) to determine the intron/exon structure in P. falciparum Dd2/Nm strain. (A) Schematic representation of the gene and predicted protein structure of baebl. Predicted protein structure has strong similarity with EBA-175, containing the putative signal sequence (SS, amino acids 1–21) predicted by SIGNALP V2.0; region 2 (two DBL domains, F1 and F2); region 6 (3′Cys), the transmembrane domain (TM, amino acids 1,134–1,153) predicted by TMHMM V2.0, followed by the putative cytoplasmic domain (Cyt). (B) f1 to f9 primers (see Materials and Methods) are used for reverse transcription–PCR of mRNA (lanes marked c) and PCR of genomic DNA (lanes marked g). (Bar = 1 kb.)