Figure 6.
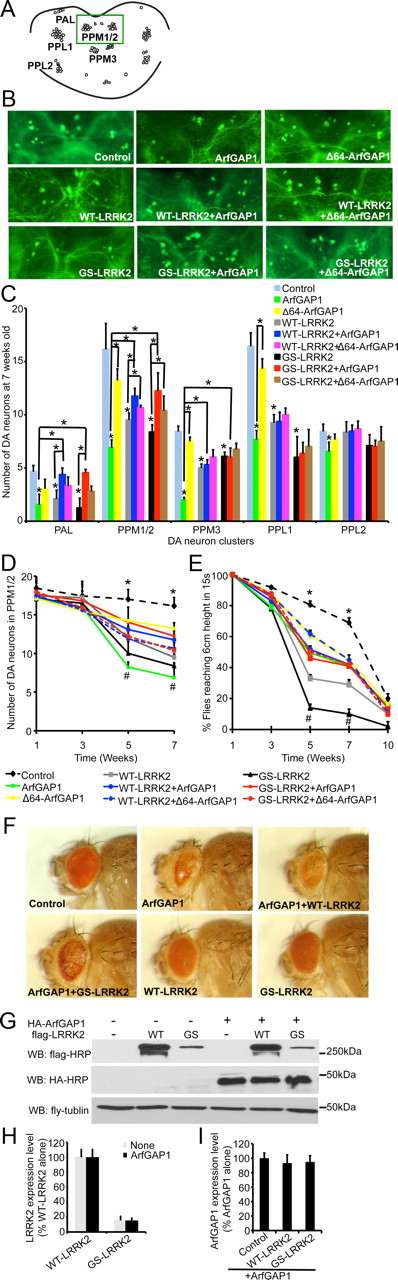
ArfGAP1 and LRRK2 genetically interact and regulate each other's toxicity in vivo. A, Diagram of dopaminergic neuronal clusters in the posterior areas of the adult fly brain. Green box shows the area selected for the images shown in B. B, Representative fluorescent images (GFP) of dopamine neurons in PPM1/2 clusters from 7-week-old flies of the indicated genotypes (green dots are neuron cell bodies). UAS–WT–LRRK2 or UAS–G2019S (GS) LRRK2, UAS–ArfGAP1 or UAS–Δ64–ArfGAP1 along with UAS–GFP were expressed in dopamine neurons by the TH–GAL4 driver. TH–GAL4>UAS–GFP was used as the control. C, Average numbers of dopamine neurons per DA cluster in 7-week- old flies of the indicated genotypes. Data represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Data were analyzed for statistical significance by two-way ANOVA (*p ≤ 0.05). D, Average numbers of dopamine neurons in PPM1/2 cluster of the flies of the indicated genotypes at different ages. Data represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Data were analyzed for statistical significance by two-way ANOVA (*p ≤ 0.05 statistically significant differences between the control and ArfGAP1, WT–LRRK2, or GS–LRRK2; #p ≤ 0.05 statistically significant differences between GS–LRRK2 and ArfGAP1+GS–LRRK2, GS–LRRK2 and Δ64–ArfGAP1+GS–LRRK2, ArfGAP1 and ArfGAP1+GS–LRRK2, WT–LRRK2 and ArfGAP1+WT–LRRK2, WT–LRRK2 and Δ64–ArfGAP1+WT–LRRK2, ArfGAP1 and ArfGAP1+WT–LRRK2, and ArfGAP1 and Δ64–ArfGAP1). E, Six groups of 20 flies from each genotype were subjected to the climbing assay every 2 weeks from 1 to 10 weeks. Data represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Data were analyzed for statistical significance by two-way ANOVA (*p < 0.05 statistically significant differences between the control and all other lines as indicated; #p < 0.05 statistically significant differences between GS–LRRK2 and ArfGAP1+GS–LRRK2, GS–LRRK2 and Δ64–ArfGAP1+GS–LRRK2, ArfGAP1 and ArfGAP1+GS–LRRK2, WT–LRRK2 and ArfGAP1+WT–LRRK2, WT–LRRK2 and Δ64–ArfGAP1+WT–LRRK2, ArfGAP1 and ArfGAP1+WT–LRRK2, ArfGAP1 and Δ64–ArfGAP1). F, Eye morphology of 1-week-old flies of the indicated genotypes. UAS–WT–LRRK2 or UAS–GS–LRRK2, UAS–ArfGAP1 were expressed in fly eyes by GMR–GAL4 driver. GMR–GAL4 is uses as the control. G, Coexpression of LRRK2 and ArfGAP1 in fly does not have significant effects on LRRK2 or ArfGAP1 expression levels. Lysates prepared form whole heads of 1-week-old flies of the indicated genotypes were subjected to immunoblotting with anti-flag–HRP, anti-HA–HRP, and anti-fly tubulin. H, Quantification of exogenous LRRK2 expression levels in fly heads. Data represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. I, Quantification of exogenous ArfGAP1 expression levels in fly heads. Data represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. WB, Western blot.
