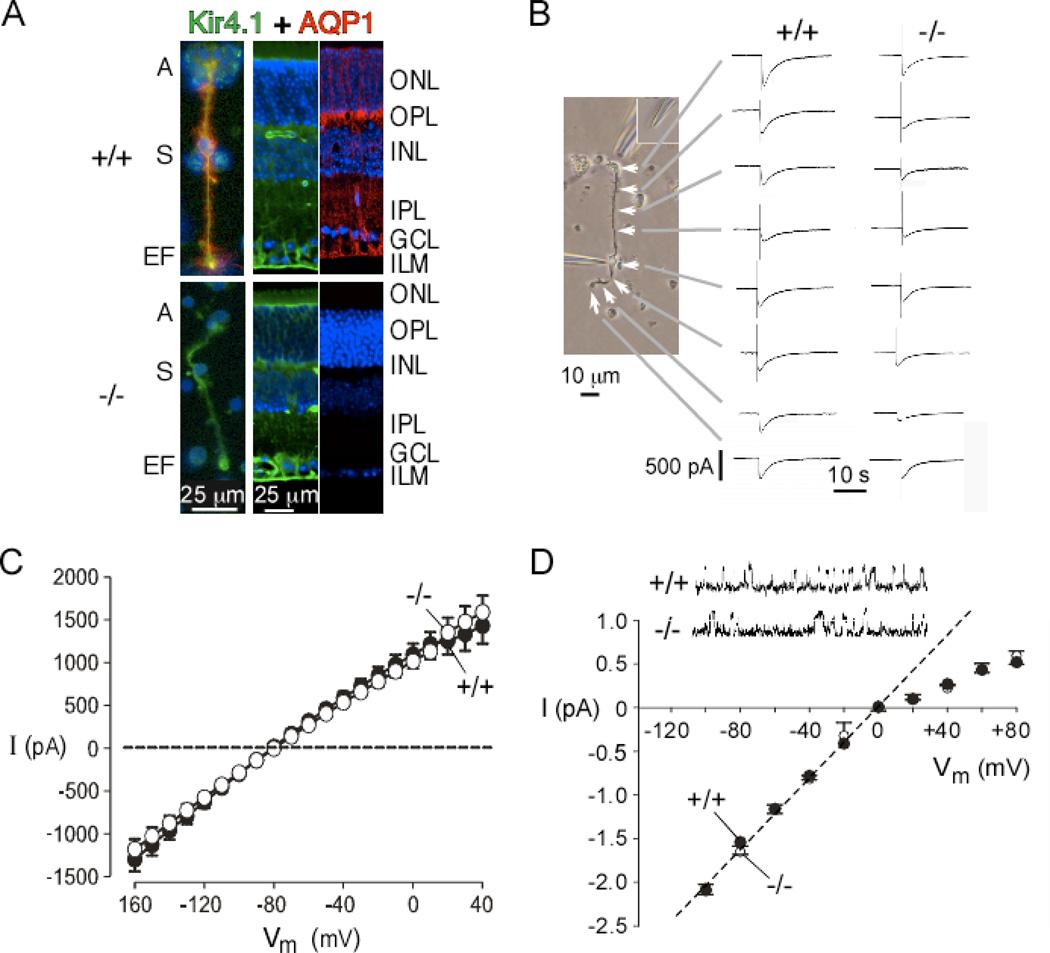
Figure 5. Kir4.1 and AQP4 are expressed in retinal Müller cells but are functionally independent.
A. (left panel) Colocalization of Kir4.1 (green) and AQP4 (red) in isolated Müller cells from wildtype (+/+, top) and AQP4 null (−/−, bottom) mice, with nuclei stained with DAPI (blue). A, apical end; S, soma; EF, endfoot. (two right panels) Retinal sections from mice. ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; ILM, inner limiting membrane. B. Spatially resolved Kir4.1 K+ conductance in Müller cells. (left) Phase-contrast micrograph showing Müller cell with soma puncture and K+ injection micropipette positioned where indicated by white arrows. Endfoot at the top and apical end at the bottom. (right) Representative whole-cell current recordings (voltage −80 mV) before and following pulsed injections of 50 mM K+ solution for wildtype (left) and AQP4 null (right) Müller cells. C. Mean current-voltage (I–V) curves of whole-cell currents in Müller cells. D. Single-channel patch-clamp of Kir4.1 K+ channels with unitary current-voltage data. Inset shows representative single-channel current traces from cell-attached membrane patches with 145 mM K+ in the pipette at −60 mV. Adapted from Ruiz-Ederra et al. (2007).