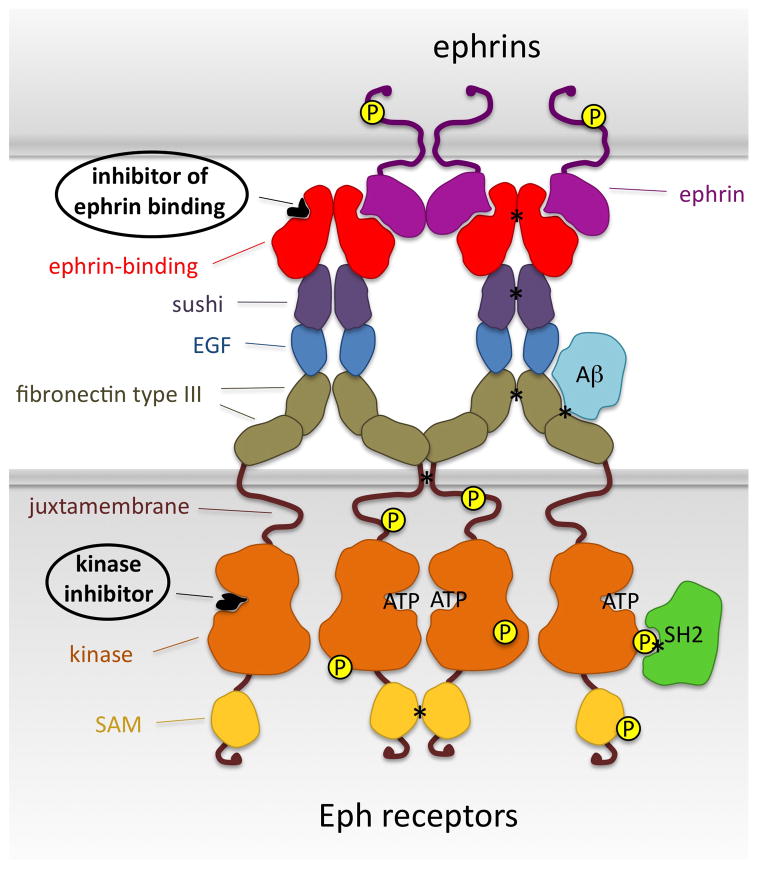
Fig. 1.
Current and potential strategies to target Eph receptors with peptides and small molecules. Molecules that target the ephrin-binding pocket inhibit ephrin binding, while molecules that target the ATP-binding site inhibit kinase activity. Other interfaces that could be targeted are those between the ephrin-binding domains, sushi domains, transmembrane segments and sterile alpha motifs (SAM) of two neighboring Eph receptor molecules (asterisks). Furthermore, inhibiting the binding of amyloid-β (A-β) or cytoplasmic signaling proteins, such as those containing SH2 domains, could more selectively affect only some Eph receptor activities.