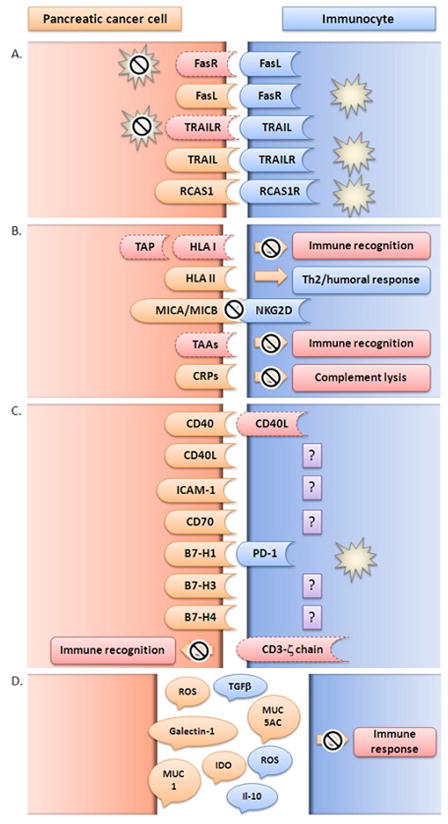
Figure 2. Mechanisms of tumor escape in PDAC development and survival.
A. Pancreatic cancer cells avoid apoptosis induced by immune cells and/or induce apoptosis in immunocytes. cancer cells manipulate ‘extrinsic’ apoptotic pathways through up-regulation of apoptotic inducing ligands (FasL, TRAIL, RCAS1) or down-regulation of apoptotic receptors (Fas, TRAILR, RCAS1R); B. Pancreatic cancer cells avoid immune detection and the effector phase of the immune response. Cancerogenesis is a dynamic sum of multiple genomic and proteomic alterations with the final result of vast heterogeneity in expression of molecules responsible for immune regulation such as HLA, MICA/MICB, TAA or CRP; C. Pancreatic cancer cells promote suppression and/or alteration of immune response. Aberrant expression of immune co-stimulatory molecules (CD40, CD40L, CD70, B7 family molecules) and adhesion molecules (ICAM-1) as well as loss of molecules necessary for immune recognition (CD3-ζ) by cancer cells leads to disruption of the immune response allowing tumor progression and invasion; D. Pancreatic cancer cells and immunocytes secrete immunosuppressive factors (TGF-β, IL-10, MUC1, MUC5AC, IDO, Galectin-1, ROS) that can dampen the immune response in the tumor microenvironment.
B7-H1 (PD-L1, programmed death-1 ligand, PD-L1); B7-H3 (CD276, co-stimulatory molecule belonging to B7 family); B7-H4 (co-stimulatory molecule belonging to B7 family); CD3-ζ (T cell co-receptor-zeta chain); CD40 (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5); CD40L (CD40-ligand, CD154); CD70 (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 7); CRP (complement regulatory protein); FasL (Fas ligand, CD95L); FasR (Fas receptor, CD95, Apo-1 tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6); ICAM-1 (inter-cellular adhesion molecule 1CD54); IDO (Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase); IL-10 (interleukin 10); HLA (human leukocyte antigen); MICA/MICB (major histocompatibility complex class I chain-related genes A and B; MUC1 (mucin 1); MUC5AC (mucin 5AC); NKG2D (natural killer cell receptor); PD-1 (programmed death 1); RCAS1 (receptor-binding cancer antigen 1); RCAS1R (receptor-binding cancer antigen 1 receptor); ROS (reactive oxygen species); TAA (tumor-associated antigen); TAP (tumor-associated antigens); TGF- β (transforming growth factor beta); Th2 (T helper type 2 lymphocytes); TRAIL (tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand); TRAILR (tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor).