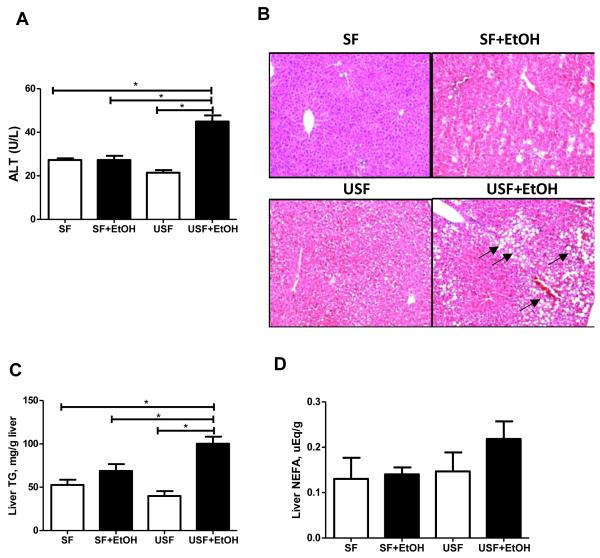
Fig. 3.
Effects of saturated and unsaturated diets on liver injury and steatosis in response to chronic alcohol feeding. (A) Liver injury was evaluated by plasma ALT activity. USF+EtOH feeding resulted in significant elevation of plasma ALT levels compared to control pair-fed animals as well as to SF+EtOH fed group (44.91+2.81 vs 21.43+1.19 and 27.27+1.92 IU/L, respectively, *p<0.05, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test). Values are mean+SEM, n=6 animals/per group. (B) Liver hematoxylin-eosin staining demonstrated severe micro- and macrovesicular steatosis in USF+EtOH fed mice compared to control pair-fed animals as well as SF+EtOH fed groups. Arrows indicate the fat droplets (x200 final magnification). (C) Significant triglyceride accumulation was observed in the livers of USF+EtOH fed mice compared to control pair-fed fed animals as well as to SF+EtOH fed group (100.2+8.1 vs 39.93+5.59 and 68.76+7.96 mg/g liver, respectively, *p<0.05, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test). (D) Liver nonesterified fatty acid (NEFA) measurement. NEFA levels were not significantly different between the experimental groups.