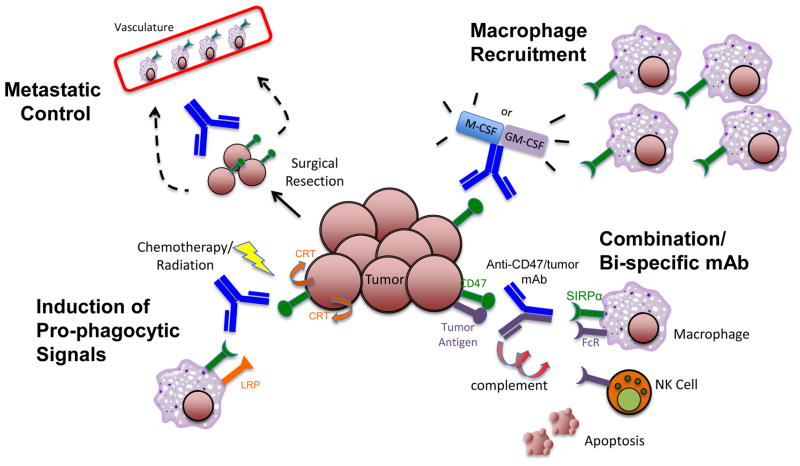
Figure 2. Combination strategies targeting CD47 in cancer.
Anti-CD47 antibody may be utilized in several combination strategies to more effectively target tumor cells. First, anti-CD47 antibody may be combined with a second antibody against a tumor-specific antigen either separately or in a bi-specific format to recruit multiple cytotoxic mechanisms: macrophage-mediated phagocytosis, NK cell mediated-ADCC, and/or CDC. Second, anti-CD47 antibody may be combined with agents that augment macrophage effector cell number and function, including M-CSF or GM-CSF, to increase effector cells at tumor sites to enable phagocytic elimination. Third, chemotherapy and/or radiation may be combined with anti-CD47 antibody to induce pro-phagocytic signals (calreticulin) on tumor cells to augment anti-CD47 antibody potency. Fourth, given the ability of anti-CD47 antibody to inhibit tumor metastasis through phagocytosis by vascular-lining macrophages or direct inhibition of chemotaxis, this therapy can be administered systemically and/or infused locally at the time of surgical excision of the tumor mass to prevent metastatic spread.