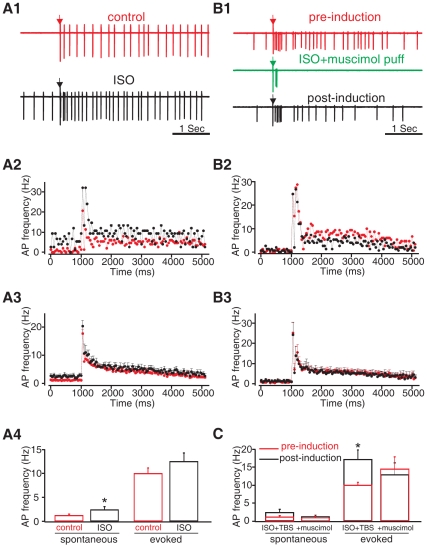
Figure 3. Glomerular application of muscimol blocked ISO+TBS induced MC spike potentiation. A1-A4.
Acute effect of isoproterenol on MC spiking. A1 . Single MC spiking patterns in the control condition and in the presence of ISO bath application. Arrow indicates the time of the single olfactory nerve test stimulus. A2&A3 . Peristimulus spike frequency histograms (binning 50 ms) under the control condition (red), in the presence of ISO (black) of the example cell in A1 (A2); and of the average of n = 7 cells in the same condition (A3). A4 . Histogram comparing mean spike frequencies during the 250 ms intervals before (spontaneous) and after the olfactory nerve stimulation (evoked) under control conditions (red) and during ISO application (black). B1-B3 . Local puff of the GABAA receptor agonist muscimol (0.2–10 µM) to the glomerular layer adjacent to the stimulation pipette during TBS blocked ISO+TBS induced MC spike potentiation. B1 . Single MC spiking patterns before, and 30 min following, TBS induction in the presence of ISO and local muscimol application. B2&B3 . Peristimulus spike frequency histograms under the control condition and 20–30 min after TBS induction in the presence of ISO and muscimol of the example cell in B1 (B2); and of the average of n = 6 cells (B3). C. Histogram comparing mean spike frequencies during the 250 ms intervals before (spontaneous) and after olfactory nerve stimulation (evoked) under control conditions (red) and 20–30 min post-inductions (black). *p<0.05. Error bars, mean±SEM.