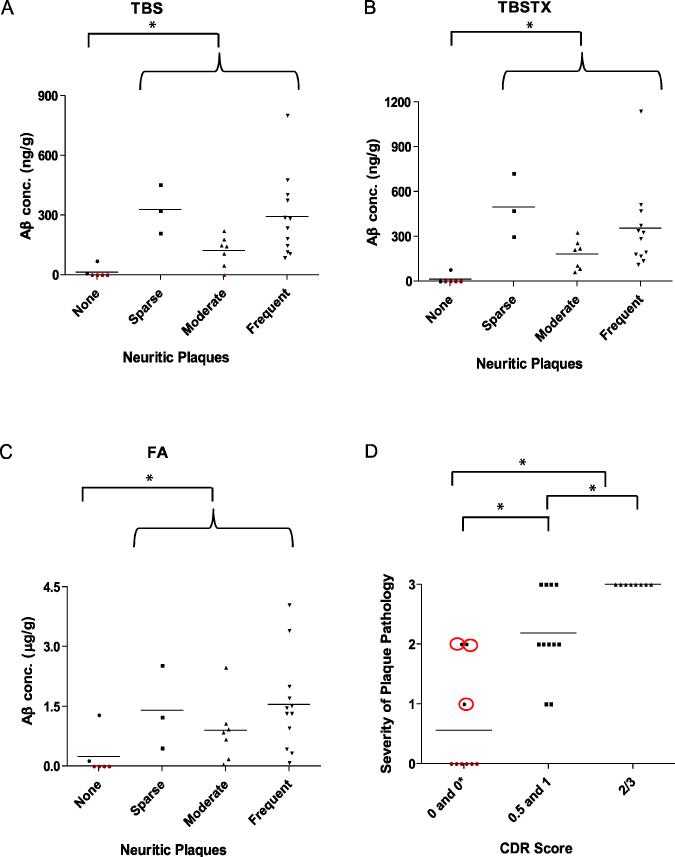
Figure 3. Levels of water-soluble and triton-soluble Aβ are increased in cases with neuritic plaques.
Total Aβ (the sum of monomer and SDS-stable dimer values) from water-soluble (A), triton-soluble (B) and FA (C) extracts were stratified based on neuritic plaque pathology. All samples with detectable Aβ are indicated in black, while those lacking Aβ are in red. The extent of neuritic plaque pathology closely correlates with severity of dementia as measured by CDR scores (D). Neuritic plaque pathology is scored from 0-3 were 0, 1, 2 and 3 represent none, sparse, moderate and frequent. All samples with detectable plaques are indicated in black, while those lacking plaques are in red. * indicates significant difference (p < 0.05). Also, Aβ levels in the TBS (A) and TBS-TX (B) extracts were significantly higher (p < 0.05) in the sparse group than in the moderate group, but were similar to the Aβ levels in the frequent group.