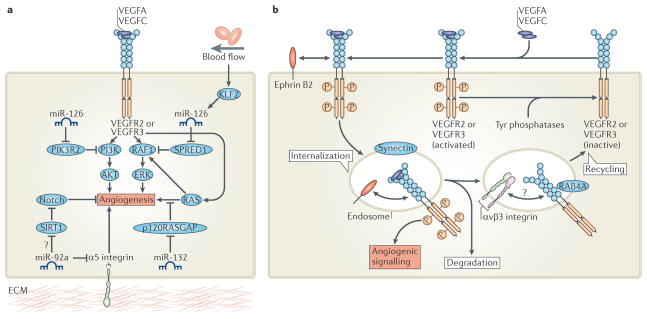
Figure 6. Fine-tuning angiogenic signals.
a | Post-transcriptional modification of key angiogenic signalling pathways by microRNAs (miRNAs) modulates angiogenesis. Expression of miR-126 de-represses phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and/or RAF1 signalling to promote vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced angiogenesis. Blood flow also influences VEGF signalling by promoting Krüppel-like factor 2 (KLF2)-induced expression of miR-126 during angiogenic sprouting. Furthermore, endothelial cell expression of miR-132 enhances angiogenic signalling controlled by RAS small GTPases by reducing the expression of RAS-specific GTPase-activating protein p120 (p120RASGAP), a negative regulator of RAS. By contrast, miR-92a blocks angiogenesis by repressing pro-angiogenic α5 integrin protein expression. miR-92a may also activate Notch signalling to block VEGF-induced angiogenesis by reducing the expression of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), which deacetylates the Notch intracellular domain to destabilize it. b | Post-translational modulation of VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2) or VEGFR3 membrane trafficking determines the duration and magnitude of VEGFA and VEGFC signalling. Synectin and ephrin B2-mediated membrane internalization protects phosphorylated active VEGFR from inactivation by cell-surface Tyr phosphatases. Furthermore, transport of VEGFR to intracellular endocytic compartments enhances pro-angiogenic signalling. Internalized VEGFR is subsequently either degraded or recycled to the cell surface for another round of activation. Hence, αvβ3 integrin and RAB4A-mediated recycling of VEGFR stabilizes receptor protein expression and enhances VEGF signalling. PIK3R2, PI3K regulatory subunit 2; SPRED1, Sprouty-related EVH1 domain-containing 1; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase.