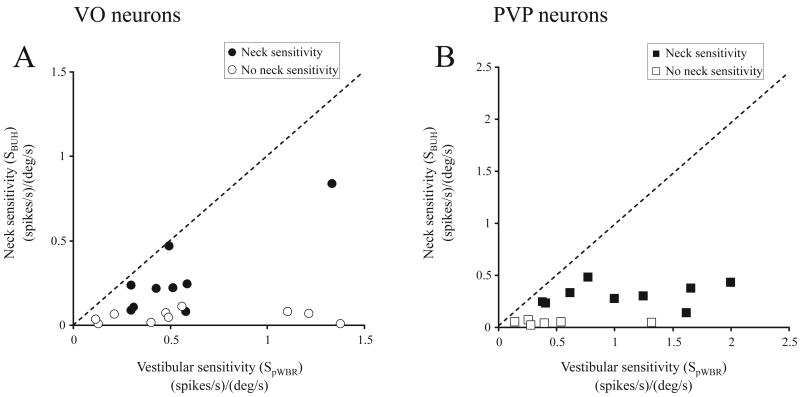
Figure 2.
Comparison of vestibular and neck proprioceptive sensitivities of VO (A) and PVP (B) neurons. The plots in A (VO) and B (PVP) depict the relationship between the calculated neuronal sensitivities (see Methods) obtained during pWBR and BUH rotations. Neurons were considered as neck sensitive (filled symbols) if this calculated neck sensitivity was greater than 0.1 (spikes/s)/(°/s) (see Methods). Note that neck proprioceptive sensitivities were, on average, ∼50% smaller than vestibular sensitivities, even for neck sensitive neurons, and as a result most of the data points fall close to the x-axis.