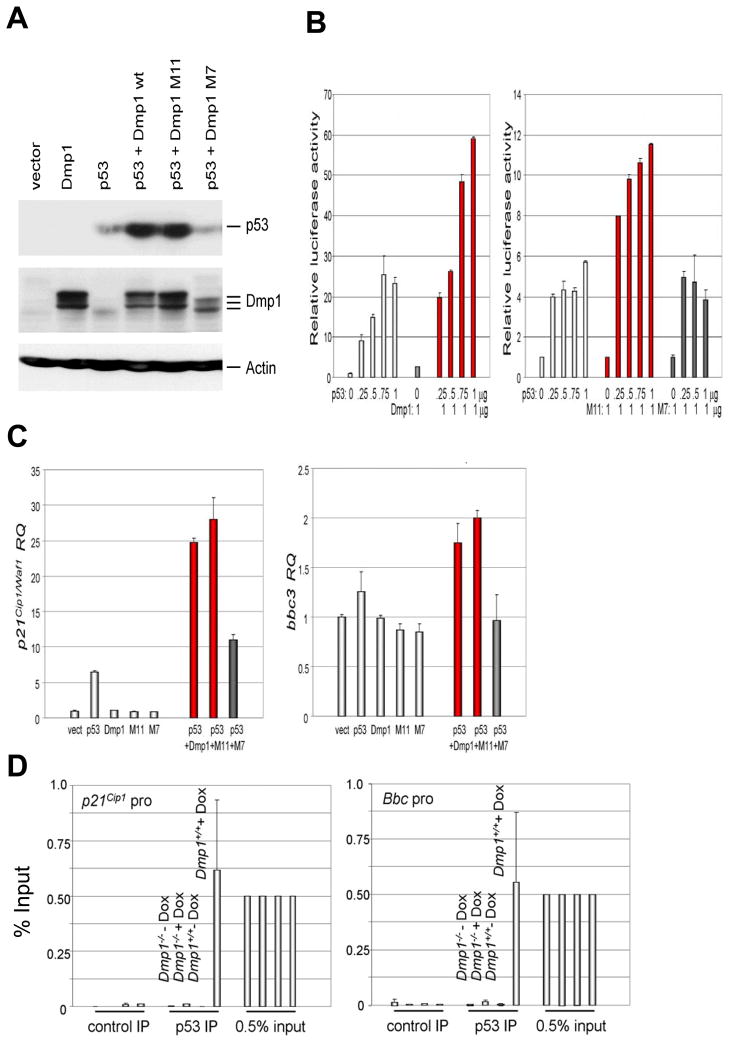
Fig. 5. Dmp1 stabilizes the p53 protein and synergizes with p53 to activate its targets in Arf-null cells.
(A) Dmp1 stabilizes p53 in Arf; p53 double knockout (DKO) mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Accumulation of p53 was observed upon co-expression of wild-type Dmp1 or M11, but not M7 indicating stability of p53 is conferred through direct binding with Dmp1 and is not a result of Dmp1’s DNA binding.
(B) Synergistic increase in p53 transcriptional target activity. Left panel: Arf; p53 DKO MEFs were co-transfected with mouse p21Cip1/Waf1 luciferase reporter and increasing doses of p53, wild-type Dmp1 only, or Dmp1 plus p53. Right panel: p21 reporter assay was conducted with M11 (DNA binding deficient) or M7 (p53 binding deficient) Dmp1 mutant plus p53. Error bars indicate SEM.
(C) Real-time PCR Taqman assay of p21Cip1/Waf1 (left) and bbc3 (right) mRNA in Arf; p53 DKO MEFs infected with retrovirus expressing p53, Dmp1, and/or Dmp1 mutants. Expression of p53 increased the p21 mRNA 7 fold, while co-expression of p53 and Dmp1 or M11 mutant induced the mRNA 25–28 fold (red bars). Synergistic induction of bbc3 mRNA by p53 and Dmp1 or M11 was also observed albeit less efficiently than p21 mRNA. The M7 Dmp1 mutant defective in p53 interaction had little effect on p21 or bbc3 mRNA induction by p53 (black bars). Error bars indicate SEM.
(D) Dmp1-dependent binding of p53 to the bbc3 and p21Cip1 promoters in mouse thymus in response to doxorubicin injection. Wild-type and Dmp1-null mice (6-week-old) were tail-injected with 0.6 mg doxorubicin/30 g mouse and thymi were harvested at 0 and 4 hrs. The binding of p53 to target gene (p21Cip1 and bbc3) promoters was studied by chromatin immunoprecipitation, followed by real-time PCR. Significant binding of p53 to the p21Cip1 and bbc3 promoters were found in wild-type, but not in Dmp1-null thymus, suggesting that Dmp1 is indispensable for p53 to bind to these promoters. Control IP: IP with protein G sepharose only.