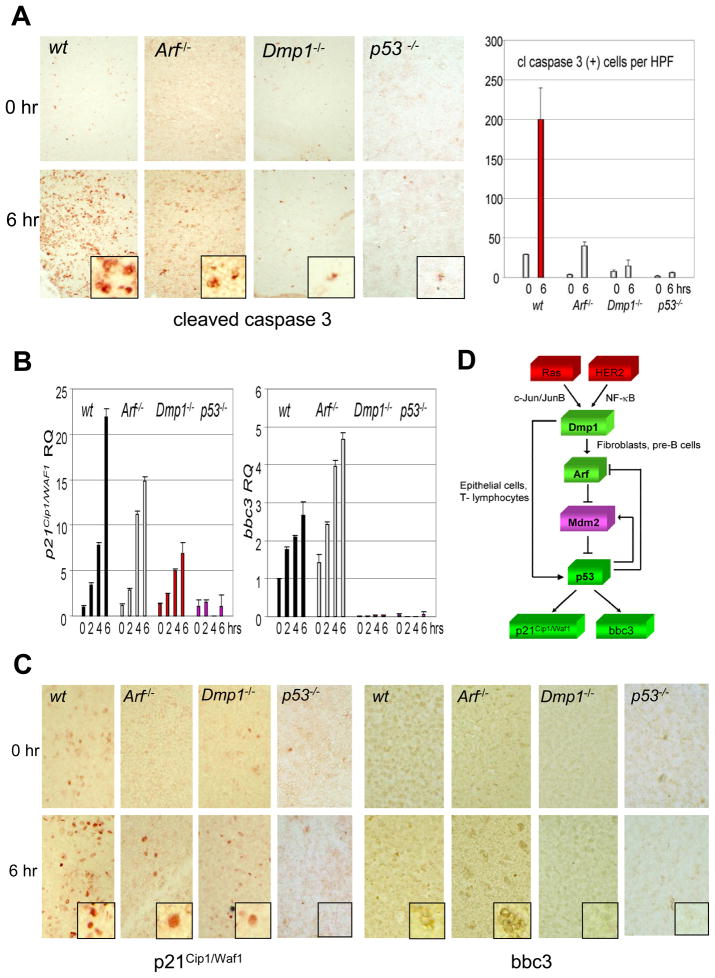
Fig. 6. p53 target gene expression in mouse thymus injected with doxorubicin and current model for the mechanism of regulation of p53 by Dmp1.
(A) Left: Cleaved caspase 3 staining of thymus from wild-type, Arf-null, Dmp1-null, and p53-null mice. Doxorubicin was injected into 6-week-old mice, and thymi were isolated before and 6 hrs after drug injection. Right: The number of cleaved caspase 3-positive cells per high power field has been counted and are shown in bar graph.
(B) Real-time PCR analysis of p21Cip1/Waf1 and bbc3 in the mouse thymus. p21Cip1/Waf1 mRNA induction was more seriously compromised Dmp1−/− or p53−/− mice than in Arf−/− mice. Bbc3 was barely detectable in Dmp1−/− or p53−/− thymi while the induction was not affected in Arf−/− mice. Error bars indicate SEM.
(C) Immunohistochemical staining of thymic tissues with p21Cip1/Waf1 and bbc3-specific antibodies showing significantly decreased induction of p53 target gene products in Dmp1−/− thymus than in Arf−/− thymus.
(D) Current model for the mechanism of regulation of p53 by Dmp1. Published studies showed that Dmp1 receives oncogenic signals from mutant Ras or overexpressed HER2 and directly transactivates the Arf promoter. This p19Arf induction, in turn, neutralizes all the activities of Mdm2 and activates p53. Our current study demonstrates that the Dmp1 protein directly interacts with p53 and blocks activities of Mdm2, especially in epithelial cells and T lymphocytes. These two mechanisms will act synergistically to boost the p53 activity to prevent tumorigenesis.