Figure 1.
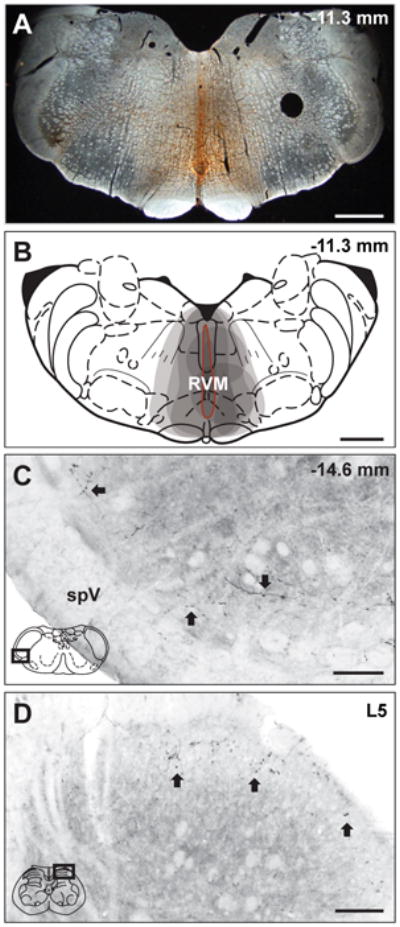
BDA injections into RVM produce anterograde labeling in trigeminal and spinal dorsal horns. (A) A representative micrograph of a BDA injection site in RVM and (B) a composite schematic illustrating individual BDA injections into RVM. (B) Each injection site is indicated by a grey shaded area, thus the darker regions represent areas included in multiple injections. All injections included the ventromedial medulla and all BDA injections into RVM resulted in bilateral labeling. The injection site outlined in red (B) represents the BDA injection site in the representative micrograph (A). (C) BDA labeling is present in representative micrographs in trigeminal (C) and spinal (C) dorsal horns. (C) BDA-labeled reticulomedullary projections were observed throughout the rostrocaudal extent of the trigeminal dorsal horn from Vi/Vc to Vc/C1 in laminae I and II as fibers with distinct varicosities (Arrows). (D) BDA-labeled reticulospinal projections were also observed as fibers and varicosities (Arrows) in laminae I and II of the lumbar spinal cord. The representative diagrams of the RVM (B), the trigeminal brainstem (C) and the spinal cord (D) are modified from the digital rat atlas of Paxinos and Watson (Paxinos and Watson, 1998) and are reproduced here with permission from the publisher. The dark rectangles in panels C and D represent the respective locations of each micrograph. The numbers on the upper right side of panels A, B and C represent the distance from bregma. In panel D, L5 refers to lumbar level 5 of the spinal cord. Scale bars: panels A and B = 1 mm; panels C and D = 100 μm. spV, spinal trigeminal tract.
