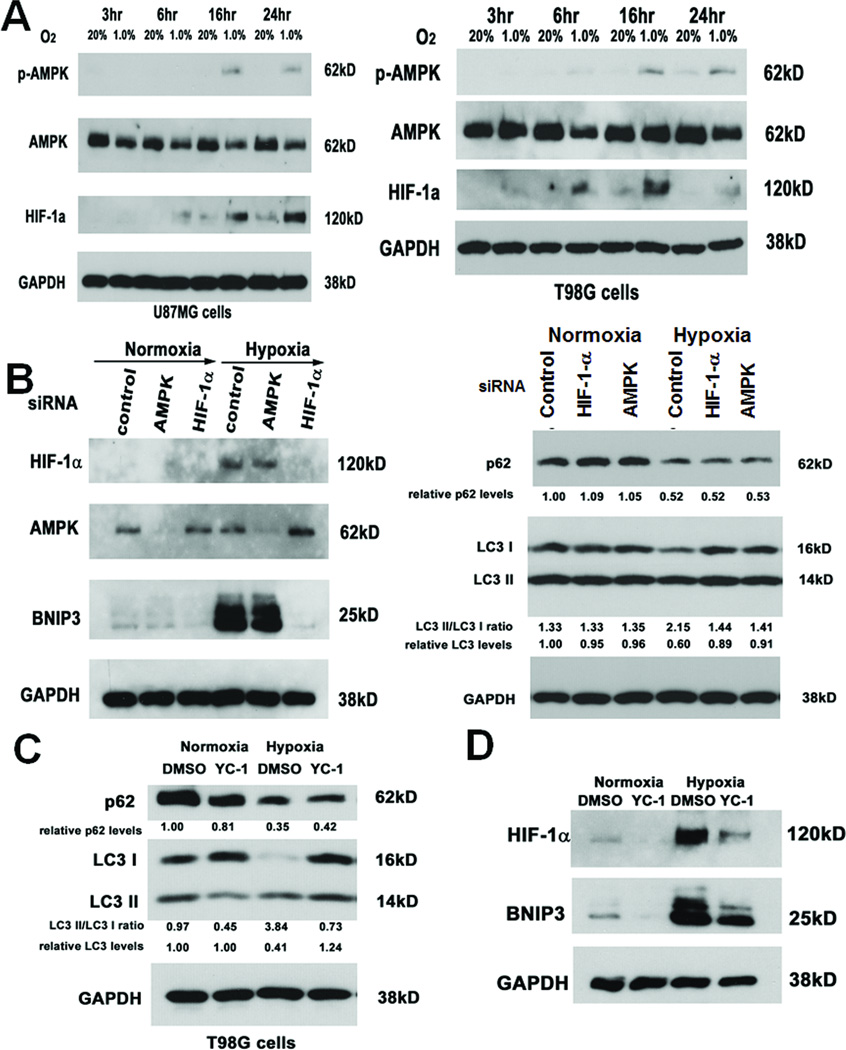
Figure 5. Hypoxia upregulates HIF-1α expression and AMPK phosphorylation, which contribute to some aspects of hypoxia-induced autophagy.
(A) U87MG and T98G cells cultured in hypoxia exhibited time-dependent activation of HIF-1α and AMPK (with AMPK activation assessed by detecting phosphorylated AMPK in the first row), with HIF-1α activation occurring before AMPK activation. (B) siRNA-mediated knockdown of AMPK and HIF-1α in hypoxic U87MG cells exhibited reduced LC3-I to LC3-II conversion and reduced total LC3 degradation but neither siRNA affected hypoxia-mediated p62 degradation, while only HIF-1α siRNA reduced hypoxia-induced BNIP3 expression. (C) Similarly, YC-1 (a HIF-1α inhibitor) blocked hypoxia-mediated LC3-I to LC3-II conversion and total LC3 degradation without affecting hypoxia-mediated p62 degradation in T98G cells. (D) In U87MG cells cultured for 24 hours in hypoxia, YC-1 blocked hypoxia-mediated BNIP3 upregulation.