Fig. (8).
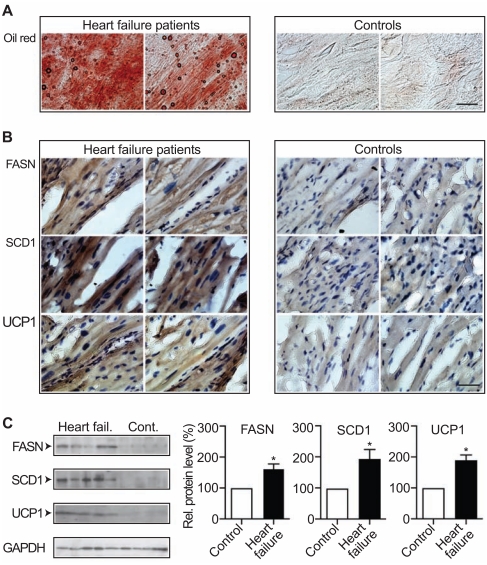
Myocardial lipid accumulation and lipid metabolizing enzymes in cardiac biopsy specimens of patients with heart failure. A. Oil red O (Oil red) staining of frozen heart sections showed cardiac lipid load in myocardial biopsy specimens isolated from patients with heart failure (Heart failure patients, n=2; left panels) compared to control patients (Controls, n=2; right panels), bar: 40 µm. B. Upper panels: immunohistological detection of FASN with F(ab)2 fragments of FASN-specific antibodies was performed in myocardial biopsy specimens of two patients with heart failure (left panels; Heart failure patients) relative to heart muscle specimens of two control patients (right panels; Controls). Middle panels: immunohistochemistry localized the key fatty acid synthesizing enzyme SCD1 in myocardial biopsy specimens of two patients with heart failure (left panels) whereas SCD1 was barely detectable with SCD1-specific antibodies in heart muscle biopsy specimens of two control patients (right panels). Lower panels show detection of high UCP1 protein levels in myocardial biopsy specimens of failing hearts (left panels; n=2) while UCP1 was almost undetectable in heart biopsies of control patients (right panels; n=2). Cell nuclei were stained with hematoxylin (bar: 40 µm). C. Left panels: Immunoblot detection of FASN, SCD1 and UCP1 in heart biopsy specimens of five patients with heart failure (Heart fail.) relative to four control patients (Cont.). As loading control, GAPDH was used. Right panels show quantifications of relative protein levels (expressed as percentage of control; %) of FASN, SCD1 and UCP1 in myocardial biopsy specimens of patients with heart failure (Heart failure; n=5) relative to control patients (Control; n=4) as determined by densitometric immunoblot blot scanning (± S.E.M.; *, p<0.05).