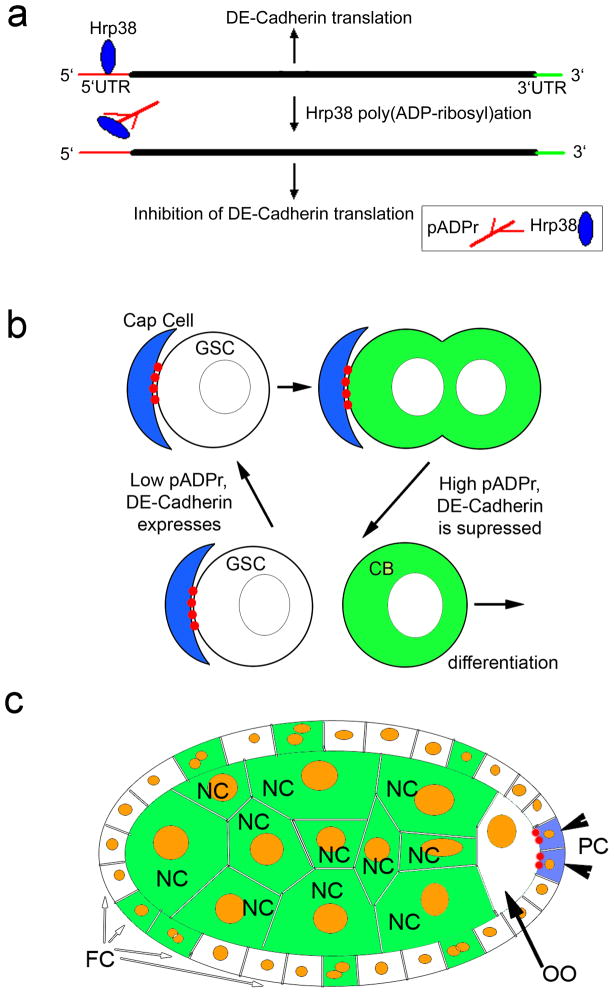
Figure 8. Diagram illustrating how Hrp38 modification by pADPr controls maintenance of GSC and oocyte localization.
(a) pADPr binding to Hrp38 regulates DE-cadherin translation. Hrp38 binds to 5′UTR of DE-cadherin to promote translation by IRES-mediated manner. Once Hrp38 is modified with pADPr and dissociated from 5′UTR of DE-cadherin, its translation is inhibited. (b) pADPr modification of Hrp38 regulates DE-cadherin translation for germ-line stem cell (GSC) maintenance. DE-cadherin (red) accumulates in the interface between cap cells and GSC, keeping GSC in the stem cell niche. High level of pADPr (green) during mitosis and in cystoblasts suppresses translation of DE-cadherin. Suppression of DE-cadherin production promotes cystoblasts to leave stem cell niche and differentiate. (c) pADPr binding to Hrp38 regulates DE-cadherin translation for oocyte (OO) localization in maturating egg chamber. Low level of pADPr in the oocyte and mitotically quiescent polar cells (PC) allows translating DE-cadherin (red) and positioning the oocyte in the posterior pole of the egg chamber. High level of pADPr (green) in nurse cells and mid-body follicle cells inhibits translation of DE-cadherin. FC - follicle cells.