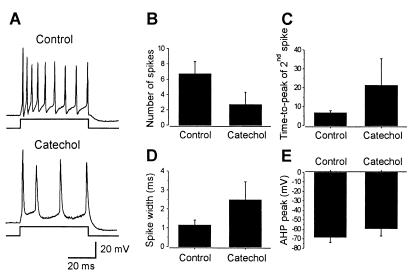
Figure 4.
Role of IA current in repetitive firing in neurons in the isolated spinal cord. (A) Application of a depolarizing current to neurons recorded in the intact spinal cord elicited repetitive firing of action potentials. Catechol reduced the repetitive firing. The neuron had a resting membrane potential of −75 mV. (B) Catechol reduced the number of action potentials elicited by current injection and increased the time to peak of the second action potential (C) and the width of action potentials (D). (E) The amplitude of the fAHP was reduced by catechol.