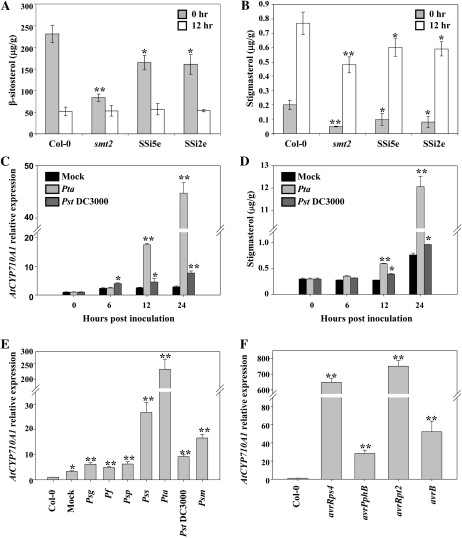
Figure 4.
Differential expression of the AtCYP710A1 gene and accumulation of stigmasterol due to plant defense. A and B, Four-week-old Arabidopsis wild-type (Col-0), smt2 mutant, and SQS1 RNAi (SSi5e and SSi2e) plants were vacuum infiltrated with a nonhost pathogen, Pta, at a concentration of 1 × 105 cfu/mL. Sterols were extracted from the leaves of inoculated plants and quantified at 12 hpi by GC-MS. C, Col-0 plants were vacuum infiltrated with 10 mm MgCl2 (mock), Pta, and Pst DC3000 at a concentration of 1 × 105 cfu/mL. Transcript levels of AtCYP710A1 were measured by qRT-PCR and the expression levels relative to 0 h (1.0) are shown. D, Stigmasterol level in the plant leaves was determined as described in B. E, Col-0 leaves were syringe infiltrated with various bacterial pathogens at a concentration of 1 × 106 cfu/mL. The relative expression of AtCYP710A1 to uninoculated Col-0 (1.0) was determined at 24 hpi by qRT-PCR. Col-0: Uninoculated; mock: 10 mm MgCl2; Pf: P. fluorescens; Psp: P. syringae pv phaseolicola. F, Col-0 plants were syringe inoculated with Pst DC3000 containing different avirulence genes (avrRps4, avrPphB, avrRpt2, and avrB) at a concentration of 1 × 105 cfu/mL. The relative expression of AtCYP710A1 to uninoculated Col-0 (1.0) was determined. Asterisks indicate a significant difference from the wild type (Student’s t test; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01). Data were pooled from two independent experiments representing four biological replicates. See also Supplemental Figures S4 and S5.