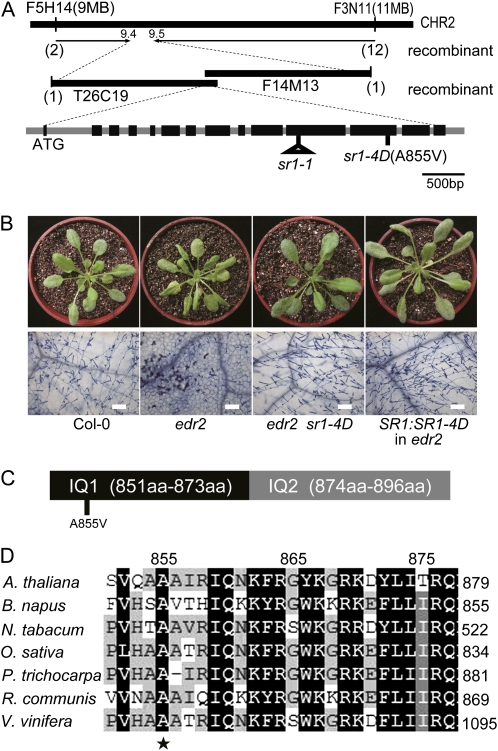
Figure 2.
SR1 encodes a calmodulin-binding transcription factor. A, Positional cloning of SR1. A nucleotide change (C2564T) in the 12th exon in At2g22300 (SR1) was identified, which led to a substitution (A855V) in the SR1 protein. B, A genomic clone of SR1 from edr2 sr1-4D suppressed edr2-mediated powdery mildew resistance. Wild-type, edr2, edr2 sr1-4D, and edr2 plants transformed with the genomic clone of mutated SR1 (derived from the edr2 sr1-4D mutant) were inoculated with powdery mildew. The plants were photographed (top panel) and stained with trypan blue (bottom panel) at 8 dpi. Bars = 100 μm. Forty-nine independent T1 transgenic plants were evaluated, and 45 of them showed an sr1-4D-like susceptible phenotype. Col, Ecotype Columbia. C, The mutation site in SR1-4D is in the first IQ motif of SR1. aa, Amino acids. D, The mutation site of SR1-4D, Ala-855, is conserved in proteins homologous to SR1 in different organisms. The SR1 protein sequence was used to perform BLAST searches against the National Center for Biotechnology Information database. SR1 and its homologs identified in different organisms were aligned using Megalign software (DNASTAR), and the alignment was further edited with Genedoc software. A. thaliana, Arabidopsis thaliana SR1; B. napus, Brassica napus accession number AAM10969.1; N. tabacum, Nicotiana tabacum accession number AAG39222.1; O. sativa, Oryza sativa accession number EEC74662.1; P. trichocarpa, Populus trichocarpa accession number XP_002310562.1; R. communis, Ricinus communis accession number XP_002519355.1; V. vinifera, Vitis vinifera accession number CBI35638.3.