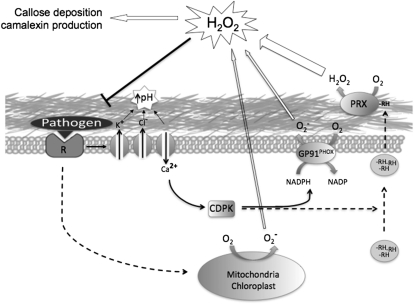
Figure 8.
Proposed model of the different components of the oxidative burst response in higher plants. Upon recognition of a pathogen, a cascade of signaling events is initiated, leading to an increase of extracellular pH, release of a reductant (RH), and activation of the cell wall peroxidases, mitochondrial ROS production, and NADPH oxidases through calcium-dependent protein kinase (CDPK)-dependent phosphorylation. Activation of these mechanisms ultimately results in an H2O2 signal that activates defense response pathways.