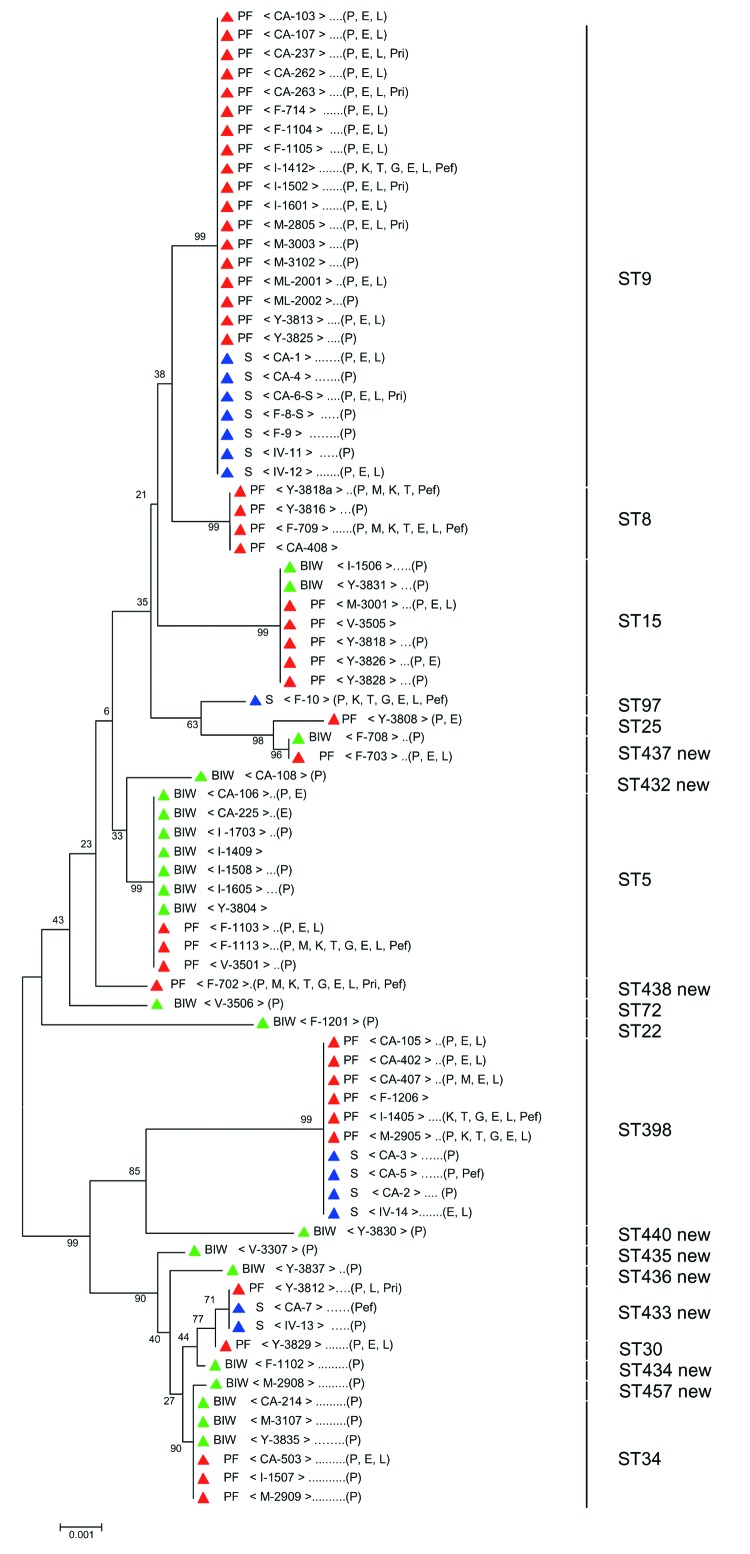
Figure.
Unrooted tree showing the phylogenetic relationships among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from pig farmers (PF), bank or insurance workers (BIW), and swine (S). The tree was obtained by the neighbor-joining method, based on the comparison of partial sequences of 7 housekeeping genes (arcC, aroE, glpF, gmk, pta, tpi, and yqiL). Values (in percentages) above the lines indicate how the tree's branches are supported by the results of bootstrap analysis. Scale bar = accumulated changes per nucleotide. Isolates from PF, BIW, and S are indicated by red, green, and blue triangles, respectively. Letters between square brackets indicate departments where strains were isolated (CA, Côte d'Armor; F, Finistère; IV, Ile et vilaine; M, Morbihan; ML, Maine et Loire;V, Vendée;Y, Yonne). Letters in parenthesis indicate the antimicrobial agents to which strains were resistant (E, erythromycin; G, gentamicin; K, kanamycin; L, lincomycin; M, methicillin; P, penicillin; Pef, pefloxacin; Pri, pristinamycin; and T, tobramycin). ST, sequence type. ST numbers shown on the right of the tree are from the S. aureus multilocus sequence typing database.