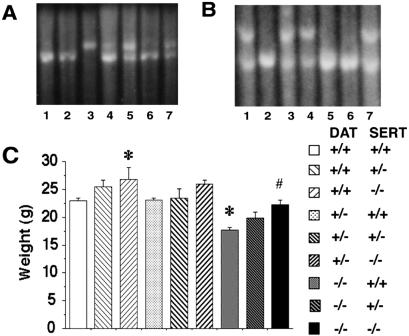
Figure 1.
Disruption of the DAT and SERT genes and effects on weights at 2 months. (A) Southern analysis of hybridization of the 3′ SERT genomic probe to KpnI-digested DNA extracted from tail tips of seven mice displaying wild-type (+/+, lane 3), heterozygote (+/−, lanes 4, 5, 7), and homozygote (−/−, lanes 1, 2, 6) patterns. The presence of an 8.1-kb fragment indicates a homozygous mutant genotype, whereas wild-type fragments are 9.6 kb32. (B) Southern analysis of hybridization of the 5′ DAT genomic probe to EcoRI-digested DNA extracted from tail tips of seven mice displaying wild-type (+/+, lane 7), heterozygote (+/−, lanes 2, 3, and 6), and homozygote (−/−, lanes 1, 4, and 5) patterns. The presence of a 5.3-kb fragment indicates the homologous recombinant genotype, whereas wild-type fragments are 6.0 kb9. (C) Weights of mice of each genotype at 8 weeks of age. Mean (± SEM; n, 5–30) values for weights were compared by using ANOVA followed by Scheffe post hoc analyses; *, significantly different from wild type; #, significantly different from DAT−/− SERT+/+; P < 0.05 for each.