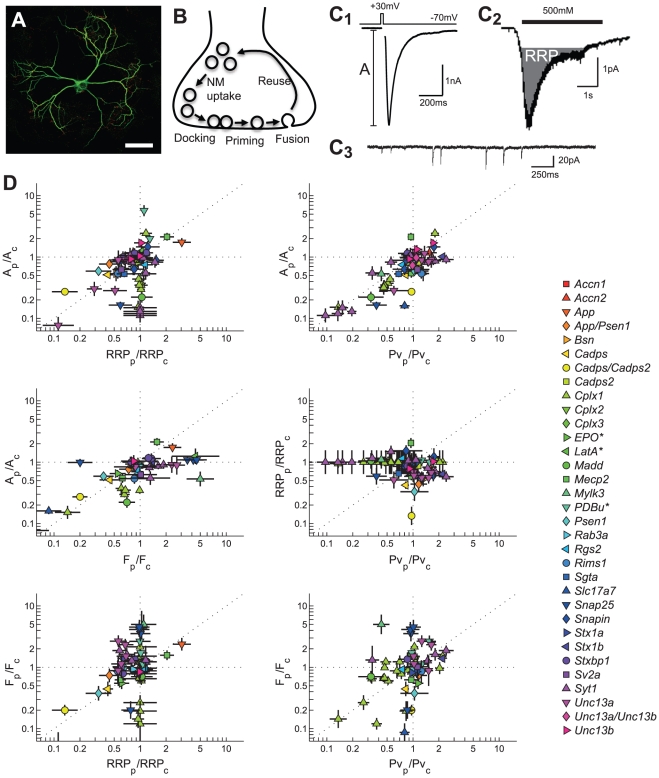
Figure 1. Functional data from genetic perturbation studies in autapses.
A) Confocal image of an autaptic neuron, scale bar is 50 µm. B) Schematic representation of a synapse. In each synapse only a limited number of vesicles, referred to as the readily releasable pool (RRP), is in a primed state that allows direct fusion during calcium triggering. The probability that a primed vesicle fuses during a calcium trigger is given by the vesicular release probability (Pv). C) Example traces of synaptic release variables. C1) Evoked EPSC (lower trace), upper trace shows somatic stimulation to trigger an action potential. C2) Postsynaptic response to a 500 mOsmol hypertonic stimulation for RRP estimation. C3) Spontaneous release events. D) Scatter plots of normalized and log-2 transformed synaptic variables in 2D projections of the 4D variable space for 121 perturbations (13 perturbations with >10-fold effect are not shown). *Non-genetic perturbations using a biochemical compound.