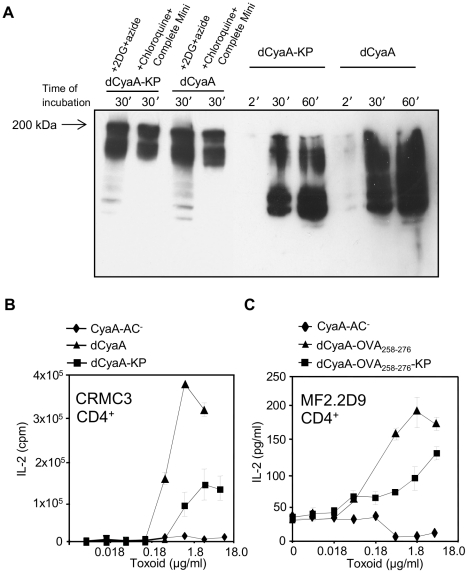
Figure 5. Macropinocytosed dCyaA-KP toxoid is rapidly degraded and its capacity to deliver epitopes for presentation on MHC class II molecules is compromised.
(A) 106 J774A.1 cells were preincubated for 30 minutes at 37°C in 1 ml of D-MEM medium alone, or in D-MEM containing 1 mM chloroquine plus a cocktail of protease inhibitors (Complete Mini, Roche), or in D-MEM containing 10 mM 2DG and 0.01% of sodium azide, respectively. dCyaA or dCyaA-KP toxoids were added to a final concentration of 1 µg/ml and after continued incubation the cells were washed three times in ice-cold D-MEM at the indicated times and lyzed on ice during 30 minutes in TBS buffer containing 1% Triton X-100 and the protease inhibitor cocktail (Complete Mini, Roche). Cell nuclei were removed by centrifugation at 13,000 RPM for 10 min and supernatants of lyzed cells were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE. CyaA fragments were detected in Western blots using the 9D4 antibody recognizing the C-terminal RTX repeats of CyaA. The arrow indicates migration of full-length (undegraded) 200 kDa CyaA. (B) BMDC from C57BL/6 mice were pulsed with indicated concentrations of dCyaA or dCyaA-KP, or (C) with dCyaA-OVA258–276 or dCyaA-OVA258–276-KP and following medium disposal, the MalE-specific hybridoma CRMC3 (B) or OVA258–276-specific hybridoma MF2.2D9 cells (C) were added, respectively. Secretion of IL-2 by antigen-stimulated CRMC3 hybridoma (B) was determined as proliferation of the IL-2-dependent CTL-L cell line and the results are expressed in cpm ± SE of duplicate samples. The concentration of IL-2 produced by MF2.2D9 cells upon antigenic stimulation (C) was determined by sandwich ELISA. A representative Western blot from 3 independent experiments and the averaged values from two independent antigen presentation experiments performed in duplicates (n = 4), are shown.